Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Critical surace tension,
γ
c
′
= 27 dyne/cm
Table 3.1.4-2 Critical surface tension values for common materials
calculated from contact angle measurements
0¼
1-methyl naphthalene drop
Dicyclohexyl drop
Material
Critical surface tension
(dyn/cm)
Methylene iodide drop
Polytetrafluoroethylene
19
90
Poly(dimethyl siloxane)
24
Water drop
Poly(vinylidine fluoride)
25
Poly(vinyl fluoride)
28
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
γ
lv
= (dynes/cm)
Polyethylene
31
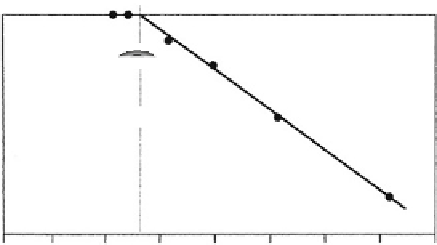
Fig. 3.1.4-4 The Zisman method permits a critical surface
tension value, an approximation to the solid surface tension, to be
measured. Drops of liquids of different surface tensions are placed
on the solid, and the contact angles of the drops are measured. The
plot of liquid surface tension versus angle is extrapolated to zero
contact angle to give the critical surface tension value.
Polystyrene
33
Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
37
Poly(vinyl alcohol)
37
Poly(methyl methacrylate)
39
Poly(vinyl chloride)
39
unique insight into how the surface will interact with the
external world. However, in performing such measure-
ments, a number of concerns must be addressed to obtain
meaningful data (
Table 3.1.4-3
). Review articles are avail-
able on contact angle measurement for surface character-
ization (
Andrade, 1985; Good, 1993; Zisman, 1964;
McIntire,
et al.
,1985
).
Polycaproamide (nylon 6)
42
Poly(ethylene oxide)-diol
43
Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
43
Polyacrylonitrile
50
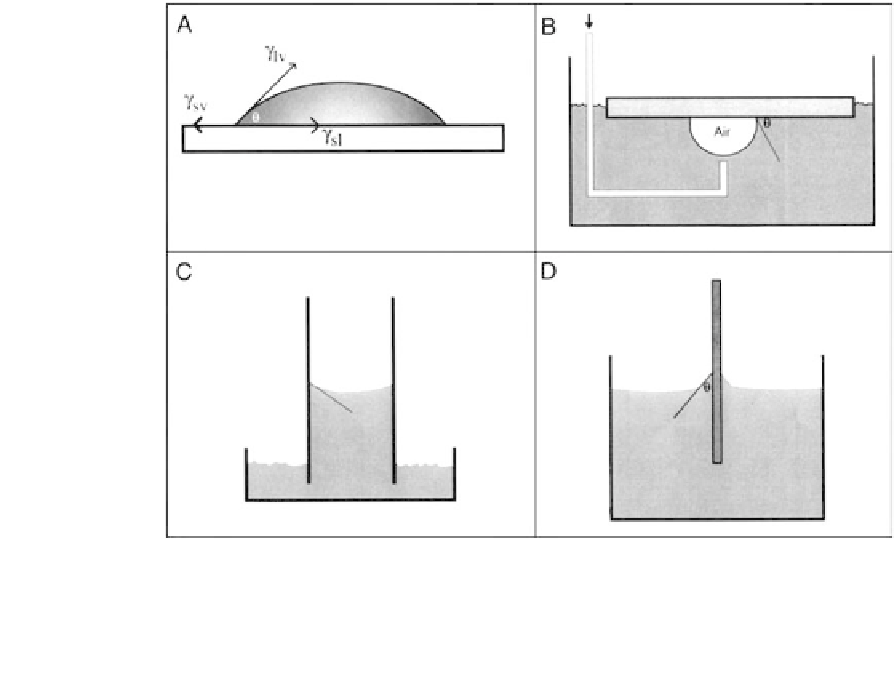
Fig. 3.1.4-5 Four possibilities for contact angle measurement: (A) sessile drop, (B) captive air bubble method, (C) capillary rise
method, (D) Wilhelmy plate method.