Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
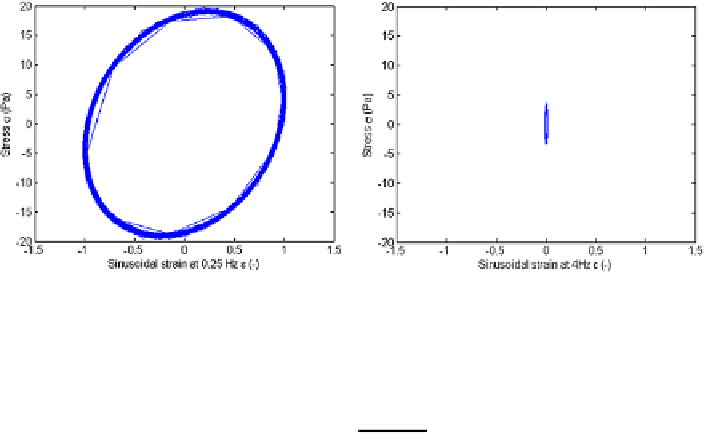
Fig. 6.12
The stress-strain curve for sinusoidal strain at
ε(t)
=
ε
0
·
sin
(
2
π
0
.
25
t)
and at
ε(t)
=
ε
0
·
sin
(
2
π
4
t)
Applying the Laplace transform on the sinusoidal strain
ε(t)
=
ε
0
·
sin
(ωt)
we have
ω
ε(s)
=
ε
0
(6.28)
s
2
ω
2
+
and the stress can be calculated as
σ(s)
E
∗
(s)ε(s)
=
L
−
1
σ(s)
(6.29)
σ(t)
=
=
=
The results for a sinusoidal strain of
ω
2
π
0
.
25 (rad/s) and of
ω
2
π
4 (rad/s) are
given in Fig.
6.12
.
As expected, the energy is dissipated and the ellipse curve is deformed to a hys-
teresis curve [
62
]. There is also a slope on this hysteresis loop, which points to the
fact that both energy storage and dissipation occurs during the test. As the frequency
increases, the loop becomes closer to the ellipse form, suggesting that viscous be-
havior becomes negligible.
The evolution with frequency of the complex modulus from (
6.27
) is depicted
in Fig.
6.13
. It is clear that the real part varies with frequency, hence if one would
identify a lumped model in a limited frequency range, would need a fractional-order
model [
67
], as explained by means of (
3.11
). Notice that in our model representa-
tion, the ladder network leads to a similar effect of constant-phase behavior as that
of the electrical ladder network in the previous chapter. This effect is visible in
Fig.
6.13
-right, below the
ω<
10
0
.
3
(rad/s) frequency range.
In a similar study, Craiem acknowledged the necessity of a fractional order to
characterize viscoelasticity in the arterial wall of the circulatory system in a sheep
[
23
]. Compared to the values in literature, one may say that our results are within
reasonable values. For example, in [
162
] the authors obtain values of 2-8 kPa for
the storage modulus, respectively values of 0.2-1 kPa for the loss modulus in guinea
pigs lung tissue strips. It is difficult to compare our results to those from [
162
],
because they come from animal studies and in general, most of the authors provide
values from tissue strips instead of an interconnected system of lung parenchymal
airways.