Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
12
9
6
3
0
Urine Collection Interval
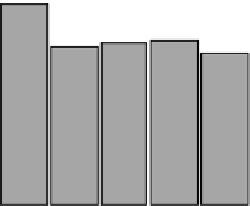
FIGURE 3.2
Urinary excretion of ANP in placebo-treated healthy subjects in a phase I
clinical study. At a mean individual urinary excretion of ANP ranging from 3.1 to 13.8 pg/mg
creatinine, the overall intrasubject variability in the urinary excretion was 22
9% CV
(mean
SD, N
¼
18) with a range from 10% to 45% CV. Arrows indicate placebo admin-
istration time (Adapted from Ref. 31, with permission).
clinical study [31]. Although the intrasubject variability of a biomarker in healthy
subjects is important to understand, it would be far more important to study the
intrasubject variability of a biomarker in the pertinent patient population. Studies of
intrasubject variability of biomarkers in patient populations would add valuable
information for the design of clinical phase II, III, and IV studies.
Evaluation of preanalytical stability of a biomarker is another key aspect that
should be addressed simulating the sample collection and handling conditions. For
example, stability of cell surface markers in shipped blood samples and physiological
variability of a marker over time are important parameters to examine for studies
that include longitudinal monitoring of marker expression. Choice of matrix, antic-
oagulant, shipment, and storage temperature should all be included in the evaluation
of stability of biomarkers that are intended to be used in clinical studies. Under-
standing the total (biological
analytical) variability in a biomar-
ker is essential for the interpretation of the biomarker results.
preanalytical
þ
þ
3.6 BIOMARKER QUALIFICATION
The qualification of a biomarker is a lengthy process where the biomarker goes
through a series of both preclinical and clinical studies with published results made
available to the scientific community. This will involve both the analytical validation












































Search WWH ::

Custom Search