Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
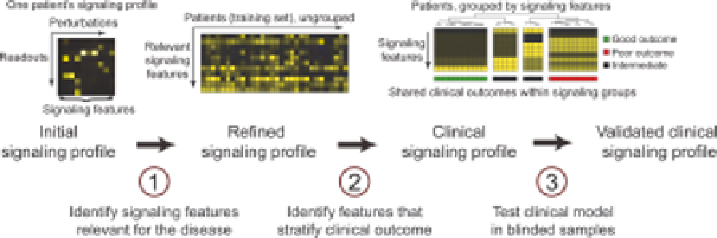
FIGURE 15.7
Creating a validated clinical signaling profile. An initial signaling profile is
obtained for each patient by measuring numerous phosphoprotein signaling events following
perturbations (stimuli and/or inhibitors) that evoke responses throughout the signaling network.
The relevance of signaling responses to the disease is judged by looking for variance in the
disease that is greater than that observed among healthy individuals. Here, a signaling feature is
the fold induction of a phosphoprotein under one of the stimulation conditions or the basal level
of the phosphoprotein. Next, features that stratify clinical outcome are identified. This can be
done in an unsupervised manner, where all relevant parameters are used, or in a supervised
manner, where features are selected based on their ability to stratify a given clinical outcome.
Finally, a simplifiedmodel using the signaling features that best stratify outcome is finalized and
then tested in a new set of patients where researchers are blinded to clinical outcome. In the end,
this approach produces a validated clinical signaling profile. (See the color version of the figure
in the Color Plates section.)
stimulation and/or inhibition, researchers vastly expand the capability to understand
and map the cell signaling network. For example, loss of signaling pathways that
control cell death, cell cycle checkpoints, and immune presentation is common in
cancer and can be a critical component of signaling pathways that stratify clinical
outcome [4]. By stimulating cells and looking for signaling events “missing” in a
patient subpopulation, one can identify the signaling equivalent of “loss of a tumor
suppressor” function [25]. In addition to revealing losses of signaling, perturbing the
signaling network can also reveal when cancer signaling networks have gained
abnormal signaling responses, such as hypersensitivity to a growth factor. In the
example of JMML, stimulation of the signaling network revealed that hypersensi-
tivity to a low dose of the cytokine GM-CSF was diagnostic for the disease [7]. Flow
cytometry measurements of phosphorylated Stat5 revealed a small population of
GM-CSF hypersensitive cells only present in patients with JMML. Combinations of
stimuli and inhibitors can also be used to map the structures of signaling networks
computationally [24]. Thus, while the resting or basal state of the signaling network
can provide valuable information, much more information is obtained through
perturbational mapping (Figure 15.8).Moving forward, signaling profiles that are
diagnostic or prognostic for a disease can be applied in preclinical or early clinical
settings. When designing a therapy based on signaling perturbation, such as inhibition
of malignant signaling, a key issue is whether targeting any one molecule is a better
strategy than simultaneously targetingmultiple signaling events identified as negative
Search WWH ::

Custom Search