Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
overwhelming, particularlywhen using proprietary reagents developed by a particular
vendor. Even with reductions in sample volume and optimization of reagent amounts,
antibodies can cost on the order of $1 per well. When we first set out to perform flow
cytometry experiments on hundreds or thousands of samples, we quickly ran into the
limitations of cost. FCB minimizes reagent consumption, enabling larger screening
efforts, disease signaling profiling experiments, and patient stratification methods
discussed elsewhere in this chapter.
15.4.1.1 The FCB Technique
The FCB technique is simple in practice [10].
Different samples are labeled with different amounts of various fluorescent dyes,
washed, and then mixed together before staining with antibodies or other reagents.
The combined sample is then run on the flow cytometer (Figure 15.4). For instance,
four wells in a 96-well plate can be labeled with none, low, medium, or high amounts
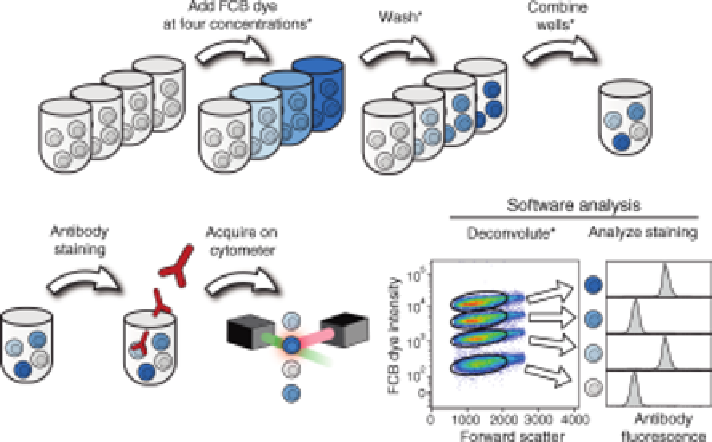
FIGURE 15.4
The fluorescent cell barcoding (FCB) method. Shown is an example where
four different samples are barcoded. In the first step, the FCB dye is added at a different
concentration to each of the four samples: none, low, medium, or high. After the cells are
covalently labeled with the dye, they are washed to eliminate free dye. At this point, the cells
are irreversibly labeled with dye, and can be combined together into one tube or well. Once
combined, the sample is treated like an ordinary sample and stained with antibodies before
acquiring on the flow cytometer. During software analysis, the four original samples
are deconvoluted, or separated, based on the intensity of fluorescence in the FCB dye channel.
Here, the four populations are gated and then analyzed for the fluorescence intensity of the
antibody staining. Expansion of the number of FCB dyes and/or dye levels enables entire
96-well plates to be combined into one sample for staining and acquisition on the cytometer,
dramatically reducing antibody consumption and increasing acquisition rates. Steps with an
asterisk (
) indicate steps unique to the FCB method relative to a standard flow cytometry
experiment.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search