Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Pattern Recognition and Discovery
Data mining is the process of identifying patterns and relationships in data that often are not obvious
in large, complex data sets. As such, data mining involves pattern recognition and, by extension,
pattern discovery. In bioinformatics, pattern recognition is most often concerned with the automatic
classification of character sequences representative of the nucleotide bases or molecular structures,
and of 3D protein structures.
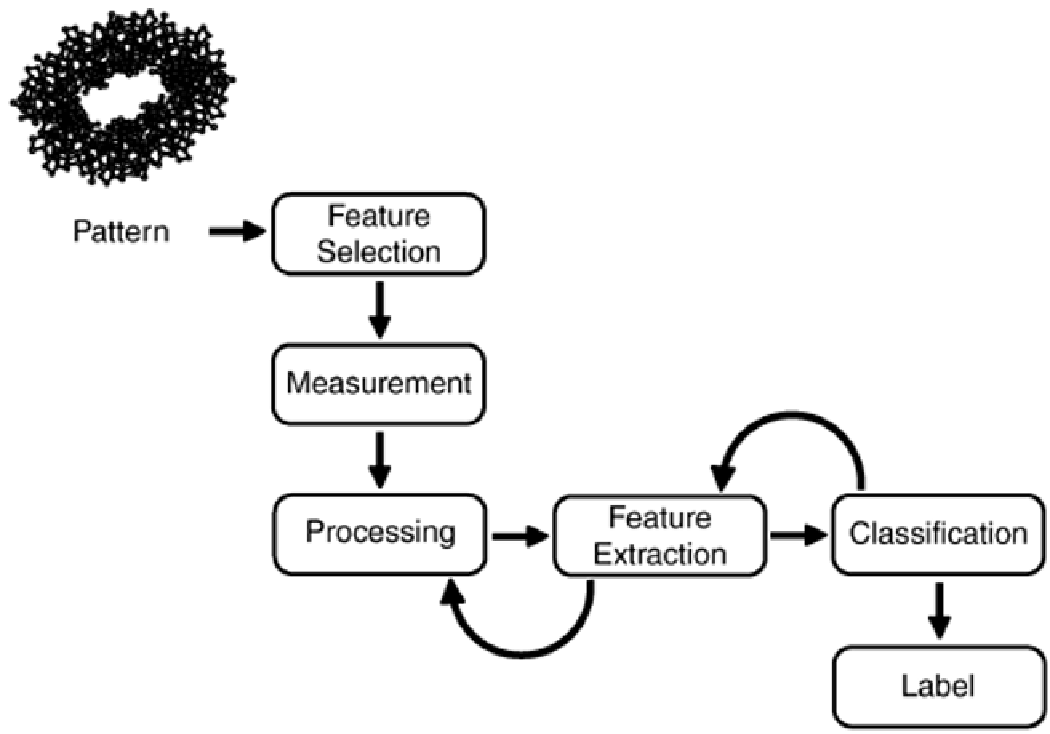
As illustrated in
Figure 7-5
, the pattern-recognition process starts with an unknown pattern, such as
a potential protein structure, and ends with a label for the pattern. From an information-processing
perspective, pattern recognition can be viewed as a data simplification process that filters extraneous
data from consideration and labels the remaining data according to a classification scheme.
Figure 7-5. The Pattern-Recognition and Discovery Process. Pattern
discovery differs from pattern recognition in that feature selection is
determined empirically under program control.
The major steps in the pattern recognition and discovery process are:
Feature Selection.
Given a pattern, the first step in pattern recognition is to select a set of
features or attributes from the universe of available features that will be used to classify the
pattern. When pattern recognition is directed at known patterns, the researcher defines a
priori the features that will be used to distinguish the pattern from other data. Feature
selection often takes the form of exemplars or representative examples of the features that
will be measured, such as the tertiary geometry of a protein. In pattern discovery, which is
more complex than simple pattern recognition, feature selection is under program control.
Instead of an a priori definition of pattern attributes defining a class or group of data that are
l