Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Clustering and Classification
Two statistical operations commonly applied to microarray data are clustering and classification.
Clustering is a purely data-driven activity that uses only data from the study or experiment to group
together measurements. Classification, in contrast, uses additional data, including heuristics, to
assign measurements to groups.
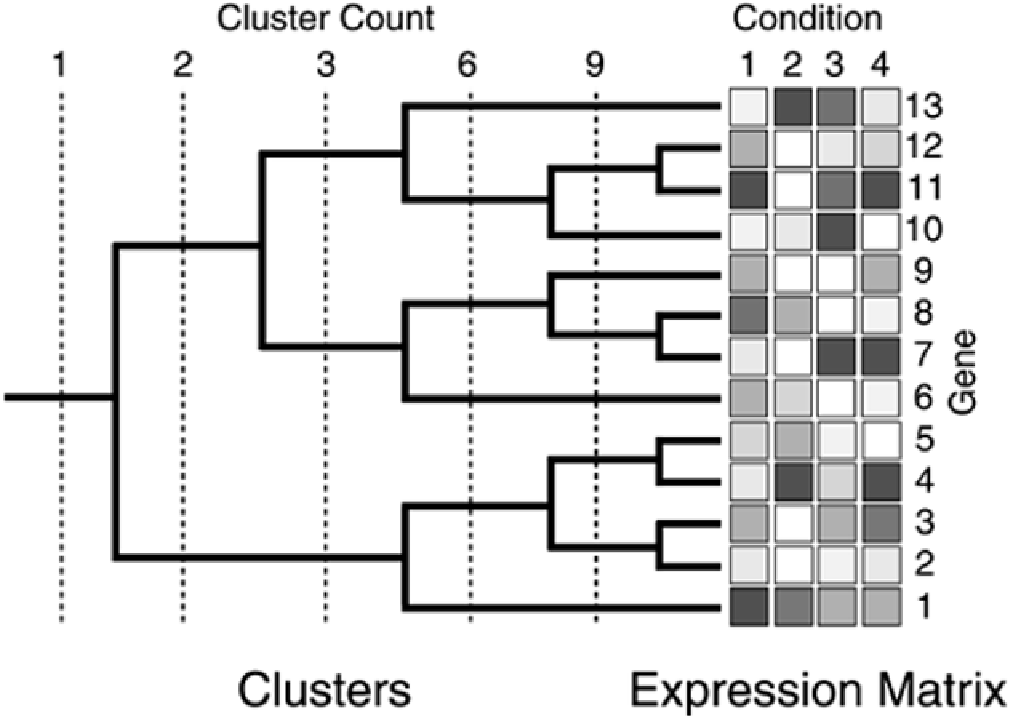
Two of the most common methods of clustering gene expression data are hierarchical clustering (see
Figure 6-22
) and k-means clustering (see
Figure 6-23
). Mathematically, hierarchical clustering
involves computing a matrix of all distances for each expression measurement in the study, merging
and averaging the values of the closest nodes, and repeating the process until all nodes are merged
into a single node. One of the many options of computing the matrix of distances involves evaluating
the relative ranking of the measures of red and green fluorescence intensities taken from the
expression matrix associated with a given microarray study.
Figure 6-22. Hierarchical Clustering. Data in the expression matrix can be
clustered to an arbitrary depth.
Figure 6-23. K-Means Clustering. Items are assigned to the nearest cluster
and the cluster centers (squares) are recalculated. This process is repeated
until the cluster centers don't change significantly. In the end, there are
two clusters, one with filled circles and one with empty circles.