Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
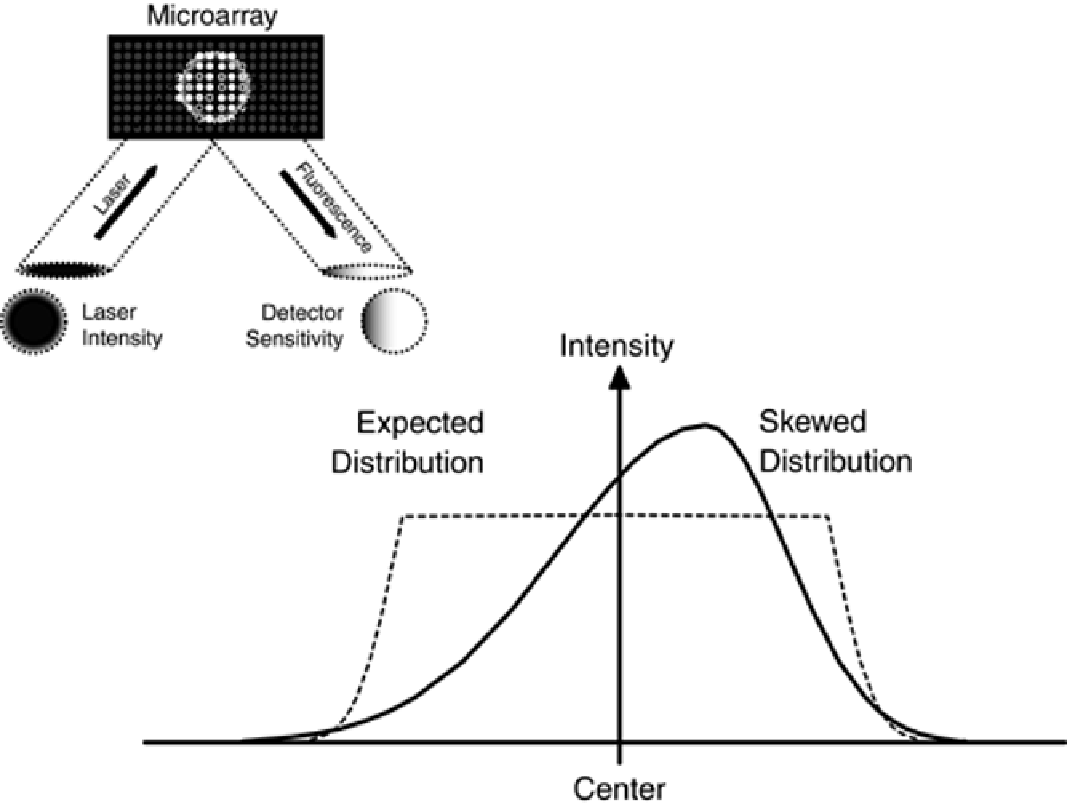
Aberrations in the exciting laser and fluorescence intensity detector in a microarray experiment result
in a peaked and skewed distribution, compared to the ideal (dotted line) distribution that is flat
across the area excited by the laser.
Figure 6-12. Deviations from the Normal Distribution. Although statistical
analysis of continuous random variables assumes a normal distribution,
many distributions are not normal, as illustrated by the skewed and
expected distributions.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing, in which a hypothesis (often termed the "null hypothesis" because it is a
negatively stated hypothesis that a researcher suspects is incorrect) is assumed to hold unless there
is enough evidence to reject it, is another basic statistical method. In microarray work, a typical
hypothesis is that two microarrays that have been subjected to the same spotting and hybridization
process will produce identical gene expression fluorescence results. The degree to which this
hypothesis is true can be estimated by examining the gene expression scatter plots created from
data gleaned from each microarray and correlating the values mathematically.