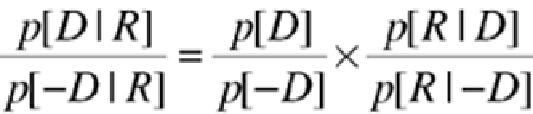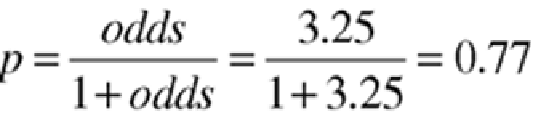Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Post-test odds = pretest odds x likelihood ratio
Expressed in the odds-likelihood form of Bayes' Theorem, this relationship appears as:
Using this equation, assume that the pretest odds of a patient having a particular genetic disease is
0.50, and that it's known that the probability that a gene expression test is positive in people with
the genetic disease is 0.65 and that the probability that the same gene expression test is positive in
people without the disease is 0.20. The post-test odds that the patient has the disease given a
positive gene expression test result is calculated as:
Converting odds to probability:
That is, the post-test odds that the patient is suffering from the disease is 0.77, up from even odds
prior to the gene expression test results. A better test—one with a greater likelihood ratio—would
have provided a greater increase in post-test odds that the patient has the disease.
The most significant limitation of Bayes' Theorem is that the input features must not only be