Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Microarrays
Microarrays offer an efficient method of gathering data that can be used to determine the expression
patterns of tens of thousands of genes in only a few hours. Microarray methods allow researchers to
examine the mRNA from different tissues in normal and disease states to determine which genes and
environmental conditions can lead to disease. Similarly, microarray methods can be used to
determine which genes are expressed in which tissues and at which times during embryonic
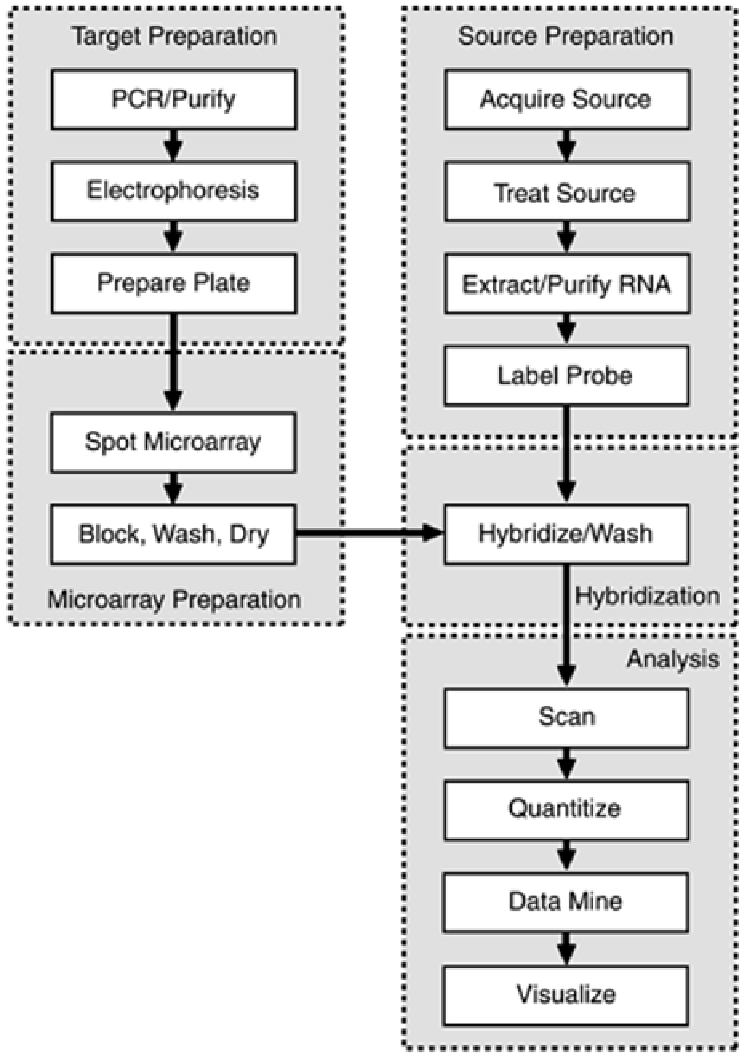
development. Spotting, the first widely used method of gene expression analysis using microarrays,
is described by the process flow diagram in
Figure 6-2
and depicted graphically in
Figure 6-3
. In
preparation for a traditional spotting microarray experiment, several microarrays are created on a
membrane, in a gel matrix, or, most often, on a scrupulously clean microscope slide made of low-
fluorescence glass. When glass slides are used as a substrate, they are coated with a non-fluorescing
compound to which known DNA sequences can easily adhere. Next, a solution containing expressed
genes is applied to (spotted on) the treated face of each slide. This spotting is performed by
mechanical robot controlled by micro pens or sprayers at a density of tens of thousands of spots per
square inch. After the spotting process, the slides are heated and dried.
Figure 6-2. Microarray Spotting Process Flow.