Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The low-level interface layer, the physical layer, is concerned with the physical input and, more
relevant as a component of visualization, physical output. With virtual reality visualization systems,
this layer includes data gloves and other devices to manipulate synthetic 3D molecules or other
objects. The physical layer also includes monitors of all types, haptic controls, speech synthesizers,
and complex mechanisms such as robotic arms.
A major component of the physical interface is the monitor. Traditional cathode ray tube (CRT)
monitors and LCD panels limit the quality of graphics and text that can be displayed. Although LCD
monitors are more space and energy-efficient, higher-end CRT monitors are considered superior for
extended use because of their higher maximum refresh rate, and greater maximum resolution,
brightness, and contrast. LCD monitors are clearly superior as head-mounted displays because of
their lighter weight and the safety afforded by their lower operating voltage. The most promising
display technology for virtual reality applications in bioinformatics uses a low-powered laser to paint
an image directly on the wearer's retina. The result is a virtual, wide-screen display in which protein
molecules or other objects appear to float in space directly in front of the wearer.
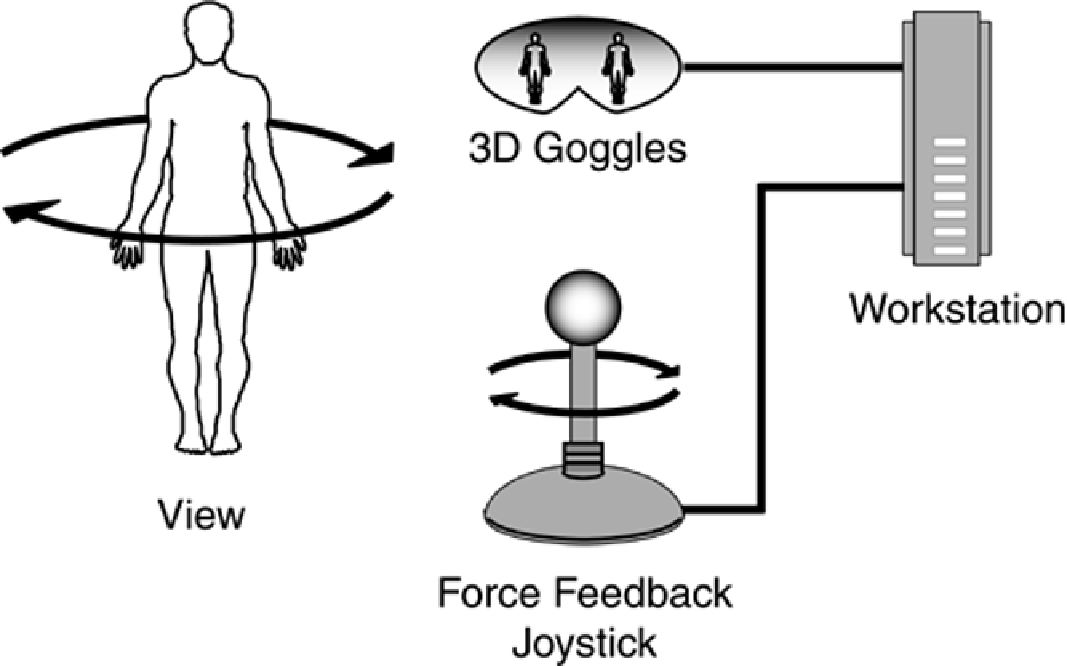
One of the more intriguing physical interface components is the haptic controller, which is a specially
constructed electromechanical mouse, or joystick, or other controller that provides the computer user
with computer-mediated tactile sensations (see
Figure 5-17
). Haptic devices use electric motors to
provide variable resistance to the movement of the controlling device, allowing users to experience
the elasticity, the viscosity, the texture of surfaces, and vibrations. In bioinformatics, the major use
of haptics is in manipulating and testing protein binding sites in a virtual reality environment, with
the amount of force provided by the interface used to provide an indication of the ease or difficulty in
manipulating the quaternary structure of a protein introducing a molecule at a particular binding site.
Figure 5-17. Haptic Joystick and Part of a Virtual Reality Workstation. Force
feedback joysticks and 3D (stereo) goggles can be used to create virtual
reality workstations in which proteins and other molecules exhibit
attraction and repulsion as they are manipulated like physical objects.
Moving up the user interface hierarchy, the graphical user interface represents everything displayed