Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
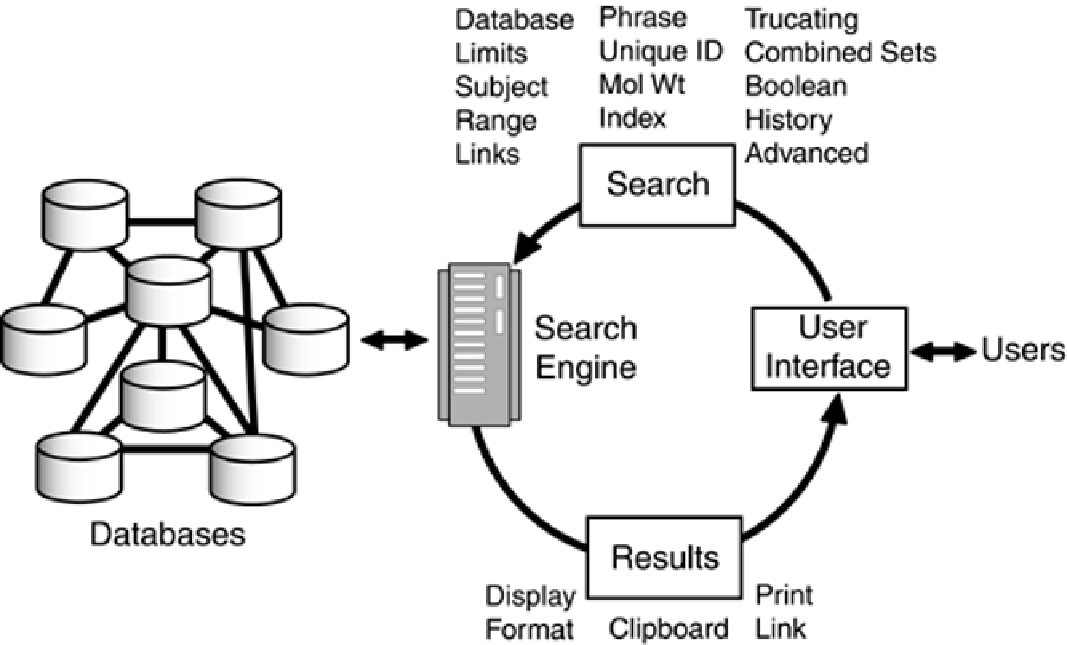
The Search
The first step in the process of initiating a search in the Entrez system is to define, through the use of
a pull-down menu system, which database to search. Once a database is selected, the next step is to
specify a search topic. Entrez supports searching by subject, subject phrase, author, unique
identifier, and, where applicable, molecular weight. Search topics are defined by keying terms into a
free-text query box. As in the most popular general-purpose search engines on the Web, such as
Google and Yahoo!, the words in a phrase are automatically treated as a Boolean AND unless they
are included in double quotes. That is, the sequence of words in a non-quoted phrase is ignored.
Conversely, a quoted phrase results in a much narrower search, because word order and position are
additional search criteria.
A search can also be specified by a unique identifier, which can be an accession number for the
complete sequence record in a database or a sequence number assigned by NCBI. The format for the
accession number depends on the database. For example, the format of an accession number in
GenBank is one letter followed by five digits, compared to a series of six or seven digits followed by a
letter for the PRF database. Entrez also supports a search based on molecular weight, including a
range of weights, based on calculations of protein structures. This search capability applies only to
the Entrez Protein database.
Regardless of the topic, searches can be narrowed and refined by the use of Boolean operators AND,
OR, and NOT, which are interpreted from left to right, except that expressions enclosed in
parentheses are evaluated first. Boolean operators are especially helpful in performing advanced,
manual searches that bypass menu-driven search choices. Complex, multi-parameter searches can
be defined by keying a search directly in the Query field.
In addition to operations on the search topics, the results of a search can be narrowed through the
use of limits. Limits can be used to restrict a search to a particular database or database field,
exclude certain types of sequences, limit the search to a particular molecule type or gene location,
only the master or only the parts of segmented sets of sequences, or by date. Limits, which can be
used singly or in combination with other limits, are defined through standard browser pull-down
menus, a free-text query box, and check boxes in the Web browser version shown in
Figure 4-5
.