Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
where symbols
c
i
are deduced from symbols
a
i
byacodingbytransition.
c
2
i
=
a
2
i
c
2
i−
1
and
c
2
i−
1
=
a
2
i−
1
c
2
i−
2
(2.100)
and
h
(
t
)
is a unit amplitude rectangular pulse shape of width
2
T
:
h
(
t
)=1
if
t
T,T
[
=0
elsewhere
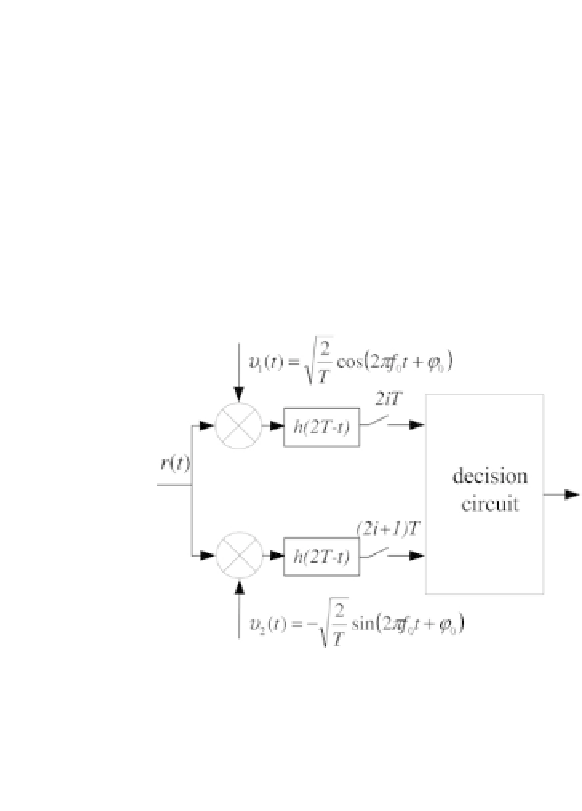
The coherent receiver for MSK is shown in Figure 2.21. It comprises two matched
filters at
h
(
t
)
with waveform
h
(2
T
∈
[
−
t
)
.Symbols
c
2
i−
1
and
c
2
i
are decoded by
comparing samples taken at the output of the matched filters, at time
2
iT
and
(2
i
+1)
T
respectively.
−
Figure 2.21 - Coherent receiver for MSK modulation.
It is easy to show that the error probabilities on binary symbols
c
2
i−
1
and
c
2
i
are identical and equal to:
2
erfc
E
b
Pe
c
i
=
1
(2.101)
N
0
where
E
b
is the energy used to transmit a binary symbol
c
i
.
To obtain binary data
a
i
from the symbols
c
i
, at the output of the coherent
receiver we have to use a differential decoder given by the following equations:
a
2
i
=
c
2
i
c
2
i−
1
and
a
2
i−
1
=
c
2
i−
1
c
2
I−
2
The bit error probability
Peb
on
a
i
is:
Peb
=1
Pe
c
i
)
2
thus for
Pe
c
i
<<
1
, a good approximation of the bit error probability
Peb
is:
Peb
−
(1
−
2
Pe
c
i
(2.102)
As a first approximation, the performance of the MSK modulation is identical
to that of the 4-PSK modulation.
≈