Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
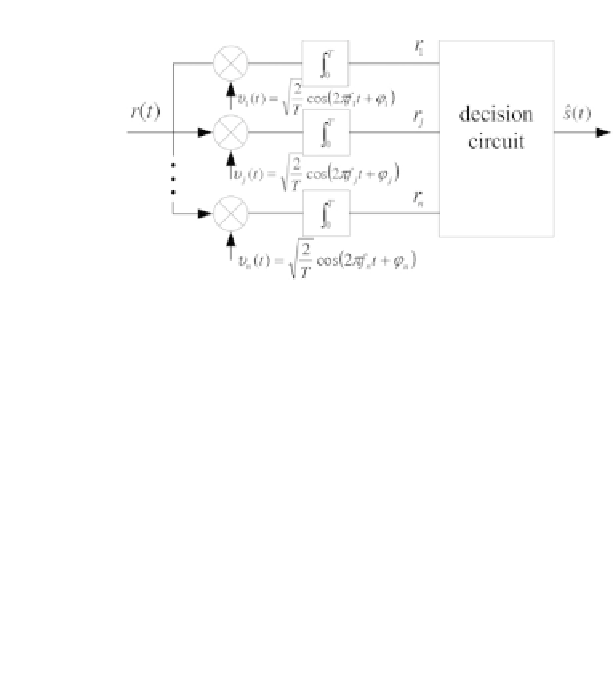
Figure 2.19 - Coherent receiver for M-FSK modulation.
where
b
j
and
b
p
are AWGN, with zero mean and variance equal to
N
0
/
2
.
The probability of a correct decision on a group of binary data, conditionally to
the emission of the signal
s
j
(
t
)
is equal to:
+
∞
Pc
j
=
Pr
{
b
1
<r
j
,
···
,b
p
<r
j
,
···
,b
M
<r
j
}
p
(
r
j
)
dr
j
−∞
The noises being non-correlated and therefore independent, since they are Gaus-
sian, we have:
⎛
⎞
M−
1
r
j
exp
db
b
2
N
0
1
√
πN
0
⎝
⎠
Pr
{
b
1
<r
j
,
···
,b
p
<r
j
,
···
,b
M
<r
j
}
=
−
−∞
and thus the probability of a correct decision is equal to:
⎛
⎞
M−
1
1
√
πN
0
r
j
exp
N
0
b
2
db
exp
E
s
)
2
dr
j
+
∞
1
√
πN
0
1
1
N
0
(
r
j
−
⎝
⎠
Pc
j
=
−
−
−∞
−∞
After changing variables, the probability of a correct decision can be expressed
as a function of the relation
E
s
/N
0
.
⎛
⎞
exp
N
0
)
2
dy
(2.88)
M
−
1
E
s
√
2
π
exp
dx
y
+
∞
x
2
2
1
√
2
π
1
1
2
(
y
⎝
⎠
Pc
j
=
−
−
−
−∞
−∞
The probability of a correct decision is the same whatever the transmitted signal.
The signals
s
j
(
t
)
being equiprobable, the mean probability of a correct decision
Pc
is therefore equal to the conditional probability
Pc
j
.
The symbol error
probability is then equal to:
Pes
=1
−
Pc