Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
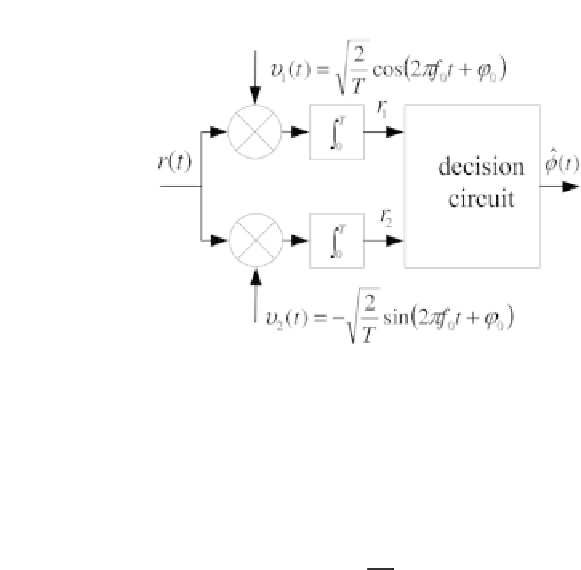
Figure 2.15 - Coherent receiver for M-PSK modulation.
binary data, whatever the value of
M
, does not have an analytical expression.
However, at high signal to noise ratios, this probability is well approximated by
the following expression:
Pes
=
erfc
log
2
(
M
)
E
b
if
π
M
E
b
N
0
N
0
sin
>>
1
(2.71)
Noting that
E
b
=
PT
b
and
D
=1
/T
b
,therelation
E
b
/N
0
is again equal to
P/N
0
D
where
P
is the received power of the modulated signal.
For Gray coding, the bit error probability with a high signal to noise ratio
is equal to:
Pes
log
2
(
M
)
E
b
N
0
Peb
=
if
>>
1
(2.72)
Case of 2-PSK modulation
For this modulation, phase
φ
j
takes the values 0 or
π
. Each phase state is
therefore associated with a bit. Adopting the following coding:
φ
j
=0
→
d
i
=1
φ
j
=
π
→
d
i
=0
the decision rule for 2-PSK modulation is simple:
d
i
=1
if
d
i
=0
if
r
1
>
0
r
1
<
0
(2.73)
Observation
r
2
is not used for decoding the data
d
i
since the space defined by
the signals modulated with two phase states has dimension
N
=1
.