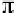Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
The coherent receiver, shown in Figure 2.13, takes its decision by comparing
observation
r
to a set of
(
M
−
1)
thresholds of the form:
2)
A
2
,
2
pA
2
,
2
A
2
,
0
,
−
(
M
−
···
,
−
···
,
−
2
A
2
,
,
2
pA
2
,
2)
A
2
(2.64)
···
···
,
(
M
−
Figure 2.13 - Coherent receiver for M-ASK modulation.
Example
Consider a 4-ASK modulation, the three thresholds being
2
A
2
,
0
,
2
A
2
.
−
Thedecisionsarethefollowing:
2
A
2
A
j
=
−
3
A
if
r<
−
2
A
2
A
j
=
−
A
if
−
<r<
0
0
<r<
2
A
2
A
j
=
A
if
r>
2
A
2
A
j
=3
A
if
The emission of a state of amplitude
A
j
corresponds to the transmission of a
group of
log
2
(
M
)
binary data
d
i
. The error probability on a group of data can be
calculated as the average value of the conditional error probabilities
Pe
2
j−
1
−M
given by:
Pe
2
j−
1
−M
=Pr
A
j
M
)
A
=(2
j
−
1
−
M
)
A
|
A
j
=(2
j
−
1
−
The mean error probability on the symbols, denoted
Pes
,isequalto:
M
1
M
Pes
=
Pe
2
j−
1
−M
j
=1
The conditional error probabilities can be classified into two types. The first
type corresponds to the probabilities that the observation is higher or is lower
than a certain threshold and the second type, to the probabilities that the