Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
R
=1
/
2
non-recursive non-systematic convolutional code with 4 states, and
with generator polynomials (5,7) in octal. Two null bits (tail-bits) are inserted
at the end of the message in order to force the termination of the trellis in state
0. Thus we obtain a sequence of 32768 coded bits, which are then randomly
interleaved and mapped into a sequence of BPSK symbols. These symbols are
transmitted on a 5-path discrete-time channel with impulse response:
h
=(0
.
227
,
0
.
460
,
0
.
688
,
0
.
460
,
0
.
227)
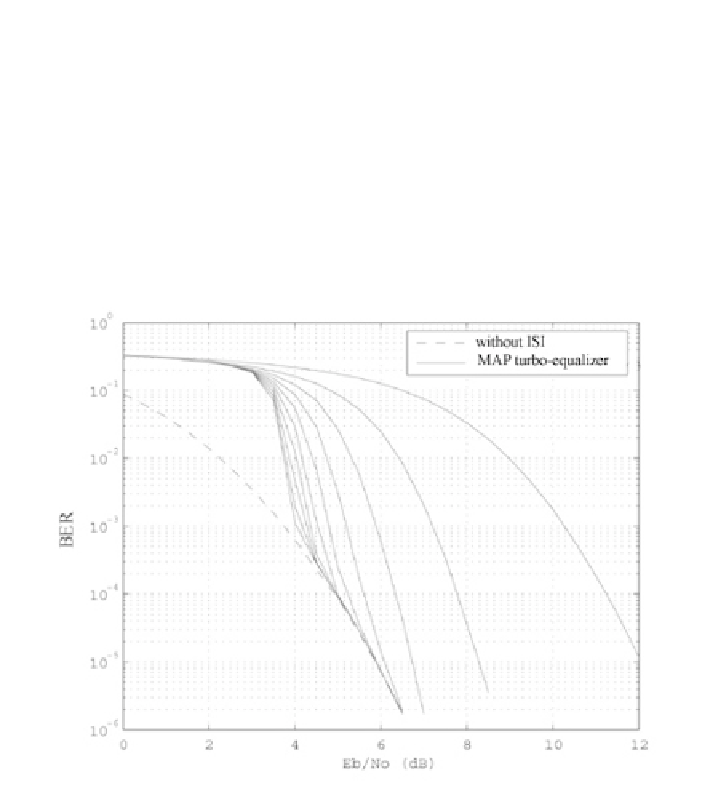
Figure 11.13 - Performance of the MAP turbo equalizer for BPSK transmission on
the Proakis C channel, using a rate
R
4-state non-recursive non-systematic
convolutional code and a pseudo-random interleaver of size 32768 bits.
=1
/
2
This channel model, called Proakis C, taken from Chapter 10 in [11.44], is
relatively dicult to equalize. At reception, we implement 10 iterations of the
MAP turbo equalizer described above. The SISO decoder is performed using the
BCJR-MAP algorithm. Figure 11.13 presents the bit error rate after decoding,
measured at each iteration, as a function of the normalized signal to noise ratio
E
b
/N
0
on the channel. For reference, we have also shown the performance
obtained after decoding on a non-frequency selective AWGN channel. This curve
shows the optimal performance of the system. We see that beyond a signal to
noise ratio of 5 dB, the turbo equalizer suppresses all the ISI after 5 iterations,
and we reach the ideal performance of the AWGN channel. Furthermore, for a