Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
a channel having
L
=3
coecients
h
=(
h
0
,h
1
,h
2
)
in the case of a binary
phase-shift-keying (BPSK) modulation.
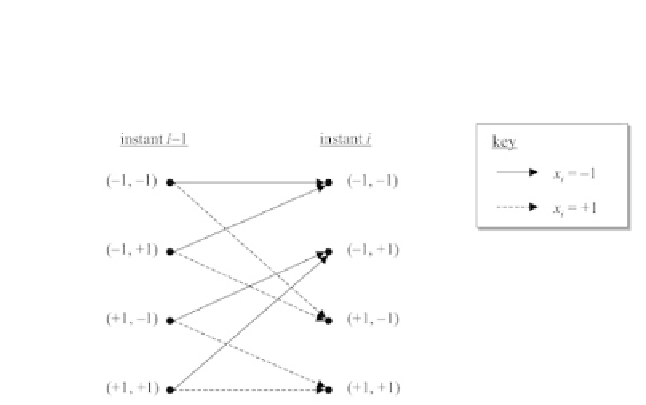
Figure 11.4 - Trellis representation for BPSK transmission on a frequency-selective
discrete-time channel with
L
=3
paths.
Each candidate sequence takes a single path in the trellis. Searching for the
sequence with the minimum Euclidean distance from the observation can then
be performed recursively, with a linear computation cost depending on the size
of the message, by applying the Viterbi algorithm on the trellis of the channel.
The MLSD equalizer offers very good performance. However, the complexity
of its implementation increases proportionally with the number of states in the
trellis, and therefore exponentially with duration
L
of the impulse response of
the channel and size
M
of the modulation alphabet. Its practical utilization is
consequently limited to transmissions using modulations with a small number of
states (2, 4, or 8) on channels with few echoes. On the other hand, it should be
noted that this equalizer requires prior estimation of the impulse response of the
channel in order to build the trellis. The MLSD solution has been adopted by
many manufacturers to perform the equalization operation in mobile telephones
for the worldwide GSM (
Global System Mobile
) standard.
In the presence of modulations with a large number of states or on channels
whose impulse response length is large, the MLSD equalizer has an unaccept-
able computation time for real-time applications. An alternative strategy then
involves combating the ISI with the help of equalizers having less complexity,
implementing digital filters.
In this perspective, the simplest solution involves applying a linear transverse
filter at the output of the channel. This filter is optimized so as to compensate
("equalize") the irregularities of the frequency response of the channel, with
the aim of converting the frequency selective channel into an equivalent ide-
ally ISI-free (or frequency-flat) channel, perturbed only by additive noise. The
transmitted message is then estimated thanks to a simple operation of symbol
by symbol decision (threshold detector) at the output of the equalizer, optimal