Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
of a product code is equal to the product of the minimum distances of the con-
stituent codes). In the case of convolutional turbo codes, the minimum distance
is not obtained analytically; the only methods proposed are based on the total
or partial [7.28] enumeration of codewords whose input weight is lower than or
equal to the minimum distance. These methods are applicable in practice only
for small sizes blocksizes and small minimum distances, which is why they will
not be described here.
Error impulse method
This method, proposed by Berrou
et al
. [7.18], is not based on the analysis of
the properties of the code but on the correction capacity of the decoder. Its
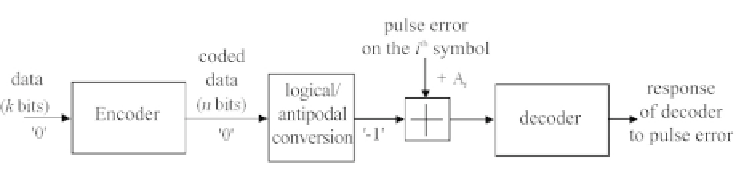
principle, illustrated in Figure 7.23, involves superposing on the input sequence
of the decoder an error impulse whose amplitude
A
i
is increased until the decoder
no longer knows how to correct it.
Figure 7.23 - Schematic diagram of the error impulse method.
The code considered being linear, the sequence transmitted is assumed to be
the "all zero" sequence. The coding operation then produces codewords that
also contain only zeros. These are next converted into real values equal to -
1. If this succession of symbols was directly applied at the decoder, the latter
would not encounter any diculty in retrieving the original message since the
transmission channel is perfect.
The proposed method involves adding an error impulse to the
i
-th symbol
(
0
≤
i
≤
k
−
1
) of the information sequence (systematic part), that is, trans-
forming a "
1+
A
i
.
If amplitude
A
i
is high enough, the decoder does not converge towards the "all
zero" word. Let us denote
A
i
the maximum amplitude of the impulse in position
i
such that the decoded codeword is the "all zero" word. It is shown in [7.18]
that, if the decoder performs maximum likelihood decoding,
impulse distance
d
imp
=min
i
=0
,··· ,k−
1
−
1
" symbol into a symbol having a positive value equal to
−
(
A
i
)
is also the minimum distance
d
min
from the code.
It is generally not necessary to test all the positions of the sequence. For a
shift invariant code (which is the case of convolutional codes), it suces to apply
the error impulse to just one position of the datablock. For a code presenting a
periodicity of period
P
, it is necessary to test
P
positions. This method is appli-