Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
In practice,
C
W
and
C
R
can be identical values
C
W
=
C
R
=
C
, typically
4 or 8. This way of introducing disorder, in small local fluctuations, does not
significantly decrease the accumulated spatial distance, whose maximum value
is
√
2
k
. However, it enables us to suppress the error patterns comparable to
those of Figures 7.6(b) and 7.7(c) on condition that the heights and widths of
these patterns are not both multiples of
C
.
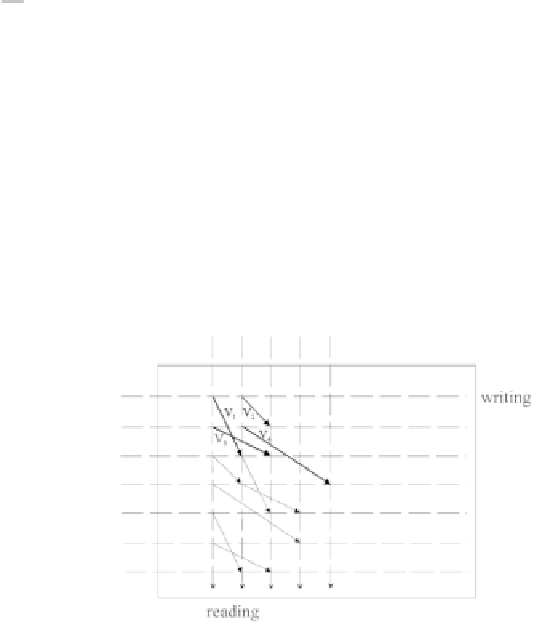
Another way to perturb the regular permutation in a controlled way is shown
in Figure 7.11. The permutation is represented here in rectangular form, visually
more accessible, but it can also be very well applied to circular permutation.
One piece of information (bit or symbol) is placed where each row and column
cross. With regular permutation, these data are therefore memorized row by
row and read column by column. In Figure 7.11, the disorder is introduced by
means of four displacement vectors
V
1
,
,V
4
that are applied alternately during
reading. These vectors have a small amplitude compared to the dimensions of
the permutation matrix.
···
Figure 7.11 - Permutation of the ARP type, following [7.17].
The mathematical model associated with this almost regular permutation,
in its circular form, is an extension of (7.4):
i
=Π(
j
)
≡
Pj
+
Q
(
j
)+
i
0
mod
k
(7.14)
If we choose
Q
(
j
)=
A
(
j
)
P
+
B
(
j
)
(7.15)
where the positive integers
A
(
j
)
and
B
(
j
)
are periodic, with cycle
C
(divisor
of
k
), then these values correspond to the positive shifts applied respectively
before and after regular permutation. That is the difference between the per-
mutation shown in Figure 7.10, in which the writing and reading perturbations
are performed inside small groups of data and not by shifts.