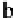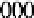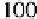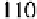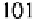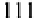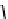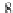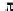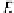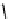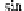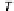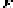Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
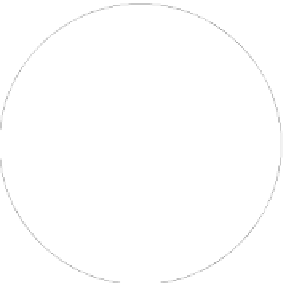
Figure 3.8 - 8-PSK constellation with Gray coding.
E
s
and
T
are the energy and the
duration of a symbol, respectively.
This relation therefore makes it possible to establish a relation between the
signal to noise ratio, the size of the information blocks and the PER. In the
same way as in Section 3.4, we can combine this result with the limits on the
signal to noise ratio to obtain the MHD targeted for a 8-PSK coded modulation
using the pragmatic approach. Figure 3.9 presents some results obtained with
this method.
3.4.3 MHD required with 16-QAM modulation
The same method as above, based on the same four hypotheses, can be applied
to the case of 16-QAM modulation with pragmatic encoding. The constellation
is a standard 16-state Gray constellation. For 75% of the bits making up the
symbols, the minimum Euclidean distance is
2
E
s
/
5
and for the remaining
25%, this distance is
3
2
E
s
/
5
. Estimating the PER gives:
2
erfc
(8
j
+
d
min
)
k
3
4
d
min
d
min
d
min
j
1
3
j
1
E
s
10
N
0
PER
≈
(3.25)
j
=0
Like for 4-PSK and 8-PSK modulations, this relation used jointly with signal to
noise ratio limits makes it possible to obtain targeted MHD values for 16-QAM
modulation (Figure 3.10).
Some observations can be made from the results obtained in Section 3.4.
For example, in the particular case of 4-PSK modulation, for a rate
R
=1
/
2
,
size
k
= 4000
bits and PER of
10
−
11
, Figure 3.6 provides a targeted MHD of
50. From the evaluation that we can make from the Gilbert-Varshamov bound