Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
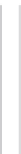
Fig. 3.5
Illustration of the
horizontal intra prediction of
a selected sample inside an
8
a
b
8 coding block with 4
4
transform blocks, if the intra
prediction is applied on the
basis of coding blocks (
a
)or
transform blocks (
b
)
prediction mode is selected for a CU and signaled inside the bitstream. The chroma
intra prediction mode applies to both chroma CBs and can be selected among five
candidates, where one of the candidates represents the intra prediction mode chosen
for the luma CB or the first luma intra block in case four intra prediction modes
are transmitted for the luma CB. The reason why the signaling of four luma intra
prediction modes is only supported for the minimum CU size is the following.
If we consider a picture block of 2
N
2
N
luma samples that is larger than the
minimum CU size, then partitioning the block into four CUs and transmitting a
luma intra prediction mode for each of the CUs is, for the luma component, the
same as coding the entire block as one CU and transmitting an intra prediction
mode for the four luma subblocks. Even though these partitioning methods do not
yield the same result for the chroma components, they can be seen as redundant
syntax features. And since the impact of coding the chroma components on the
overall coding efficiency is usually very small, the corresponding redundant syntax
is avoided and a subdivision of the luma CB for signaling intra prediction modes is
only supported for the minimum CU size.
The actual intra prediction is not always applied to the blocks for which the intra
prediction modes are signaled. A coding block can be split into multiple transform
blocks, which represent the units to which a single two-dimensional transform is
applied for coding the prediction residuals. As will be discussed in Sect.
3.2.4
,the
subdivision of the coding blocks of a CU into transform blocks is specified by a
second quadtree structure, for which the CU represents the quadtree root. If a luma
CB is subdivided into four subblocks for signaling the intra prediction modes, it
is also subdivided for the purpose of transform coding so that all samples inside
a transform block are always predicted using the same intra prediction mode. It is,
however, possible that a block for which a single intra prediction mode is transmitted
is further partitioned into multiple transform blocks. Since the correlation between
two image samples decreases with the distance between the samples (for any given
direction), on average, a better prediction signal is obtained if we use reconstructed
samples that are closer to the samples we want to predict. Due to this reason, the
intra prediction is done on the basis of transform blocks. The effect is illustrated
in Fig.
3.5
for the example of horizontal intra prediction of an 8
8 coding block
that is split into 4
4 transform blocks. It should be noted that, on the one hand
side, the efficiency of intra prediction decreases with increasing the size of the
transform blocks, since the average distance between a predicted sample and the
reference samples used for prediction increases. On the other hand side, however,