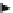Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
B
3
B
4
*
B
7
*
B
8
*
B
6
*
B
2
I
0
P
1
*
I
5
Fig. 2.10
Sub-layer reference and sub-layer non-reference pictures
2.2.2.11
Reserved and Unspecified VCL NAL Unit Types
In addition to the VCL NAL unit types described above, Table
2.1
contains
several reserved VCL NAL unit types, which are divided into IRAP and non-
IRAP categories. These reserved values are not allowed to be used in bitstreams
conforming to the version 1 specification, and are intended for future extensions.
Decoders conforming to version 1 of HEVC must discard NAL units with NAL
unit types indicating reserved values. Some NAL unit types are also defined as
“unspecified”, which means they can be used by systems to carry indications or
data that do not affect the specified decoding process.
2.2.3
Coded Video Sequences and Bitstream Conformance
A coded video sequence (CVS) in HEVC is a series of access units that starts with
an IDR or BLA access unit and includes all access units up to but not including the
next IDR or BLA access unit or until the end of the bitstream. A CVS will also start
with a CRA access unit if the CRA is the first access unit in the bitstream or if the
decoder is set to treat a CRA picture as a BLA picture by external means.
A bitstream is a series of one or more coded video sequences. The bitstream can
be in the form of a NAL unit stream, which is a sequence of NAL units in decoding
order, or in the form of a byte stream, which is a NAL unit stream with special fixed-
value strings called “start codes” inserted in-between the NAL units. The boundaries
of the NAL units in a byte stream can be identified by scanning for the start code
string values, whereas a NAL unit stream requires some extra framing information
to be provided by a system environment in order to identify the location and size of
each of the NAL units in the stream.
In order for a bitstream to conform to the HEVC specification, all requirements
and restrictions in the HEVC specification must be fulfilled. All syntax restrictions
must be met, for example the temporal ID of IRAP NAL units must be equal to 0.
Data that does not conform to the HEVC specification can be simply rejected
by decoders; the standard does not specify what a decoder should do if such
data is encountered. Non-conforming data may be the result of problems in a