Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 10.14
Chip specifications
Technology
TSMC 40 nm CMOS
Supply Voltage
Core: 0.9 V, I/O: 2.5 V
Chip Size
2:18mm 2:18mm
Core Size
1:33mm 1:33mm
Gate Count
715K (2-input NAND)
On-Chip SRAM
124 kB
Maximum Throughput
249 Mpixel/s @ 200 MHz
Decoding Tools
HEVC WD4 (HM 4.0 low complexity w/o SAO)
CTU size: 64
16
B-frame: Low Delay(LD)/Random Access(RA)
Symmetric and asymmetric motion partitions: 4
64, 32
32, 16
4
64
64
Square and non-square transform units: 4
4
32
32
All intra modes: DC, Planar, 33 Angular, LMChroma
Measured Core Power
76 mW @ 0.9 V 200 MHz, 3840
2160 @ 30fps (average)
51 mW @ 0.9 V 100 MHz, 1920
1080 @ 60fps (average)
31 mW @ 0.9 V 25 MHz, 1280
720 @ 30fps (average)
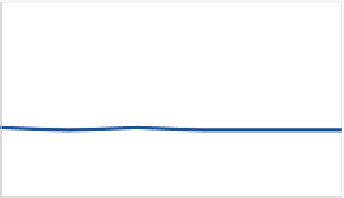
Fig. 10.23
Core power is measured for six different combinations—Random Access and Low
Delay encoder configurations each with all three sizes of coding tree units. The core power is more
or less constant due to our unified design
Length Coding (CAVLC) is used in place of CABAC in the Entropy Decoder.
This chip achieves 249 Mpixels/s decoding throughput for 4K Ultra HD videos at
200 MHz with the target DDR3 SDRAM operating at 400 MHz. The core power is
measured for six different configurations as shown in Fig.
10.23
. The average core
power consumption for 4K Ultra HD decoding at 30 fps is 76 mW at 0.9 V which
corresponds to 0.31 nJ/pixel. Logic and SRAM breakdown of the chip is shown in
Fig.
10.24
. Similar to H.264/AVC decoders, we observe that prediction has the most
significant resource utilization. However, we also observe that inverse transform is
now significant due to the larger transform units while deblocking filter is relatively
small due to simplifications in the standard. Power breakdown from post-layout
power simulations with a bi-prediction bitstream is shown in Fig.
10.25
. We observe