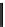Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 8. 12
Binarization of the absolute level
z
for the choice of parameters B
0
D
2, B
1
D
6,and
k
D
0, corresponding to a concatenation of TrU with cMax
D
3, zero-order Truncated Rice (TRk)
with cMax
D
4, and first-order Exp-Golomb (EGk)
TrU
TRk
EGk
cMaxD3
k D 0;cMaxD4
k C 1 D 1
z
SIG
ALG1
ALG2
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
...
0
0
1
1
0
B
0
D
2
1
1
0
3
1
1
1
0
4
1
1
1
10
5
1
1
1
110
B
1
D
6
1
1
1
1110
7
1
1
1
111100
8
1
1
1
111101
9
1
1
1
11111000
10
1
1
1
11111001
11
1
1
1
11111010
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
all absolute levels
z
in each subblock. As a consequence, the majority of resulting
bins can be simply bypass coded without compromising coding efficiency.
For each subblock, the initialization and adaptation processes for the parameters
B
0
;B
1
,andk is performed, as follows. Before starting the processing of an
subblock, the parameter k is set equal to 0, whereas B
0
is set equal to 2. The
second thresholding parameter B
1
depends on k and B
0
by the fixed relation
B
1
D
4
2
k
C
B
0
, which means that B
1
is adapted whenever B
0
or k are changed. For
each scan position in the subblock processing, the absolute level
z
is evaluated after
encoding/decoding and B
0
is decremented by 1 after the first occurrence of
z
>1,
which corresponds to the first scan position in the subblock for which an ALG2 flag
is signaled. A further adaptation of B
0
to its minimum value of 0 is performed after
z
>0, i.e., after an ALG1 flag occurs eight times in the subblock. The parameter k
is set to min.k
C
1; 4/ after each scan position for which the corresponding absolute
level
z
fulfills the condition
z
>3
2
k
. Note that according to this adaptation rule,
k can take integer values from 0 to 4 inclusive. Tables
8.12
and
8.13
show example
binarizations for two different configurations of the parameters B
0
;B
1
,andk. Please
note that the result of the binarization for
z
can also be interpreted as a concatenation
of a unary prefix and, if present, a fixed-length suffix for different ranges of
z
[
21
].
Tab le
8.14
shows the corresponding binarization of ALRem, which has a maximum
bin length of 32 [
12
].
As already indicated above, the signaling of the absolute level
z
involves
four different syntax elements, given as
sig_coeff_flag
(SIG),
coeff_abs
_level_greater1_flag
(ALG1),
coeff_abs_level_greater2_flag
(ALG2), and
coeff_abs_level_remaining
(ALRem), such that
z
D
SIG
C
ALG1
C
ALG2
C
ALRem;