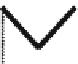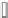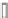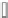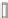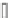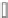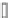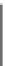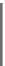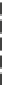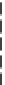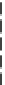Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 7. 2
Sample category
classification rules for edge
offset
Category
Condition
1
c < a&&c< b
2
(c < a&&c
DD
b)
jj
(c
DD
a&&c< b)
3
(c > a&&c
DD
b)
jj
(c
DD
a&&c> b)
4
c > a&&c> b
0
None of the above
Category 1
Category 2
Category 3
Category 4
value
value
value
value
acb
ac b
acb
ac b
sample index
sample index
sample index
sample index
value
value
ac
b
ac
b
sample index
sample index
Fig. 7.15
Positive offsets for EO categories 1 and 2 and negative offsets for EO categories 3 and 4
results in smoothing, where the x-axis is sample index and the y-axis is sample value. Reproduced
with permission from [
13
], © 2012 IEEE
The effect of the positive and negative edge offsets is illustrated in Fig.
7.15
and explained as follows. Positive offsets for categories 1 and 2 result in smoothing
since local valleys and concave corners become smoother, while negative offsets
for these categories result in sharpening. On the contrary, for categories 3 and 4,
the negative offsets result in smoothing and positive offsets result in sharpening.
In HEVC, sharpening in EO is not allowed. Therefore, the absolute values of four
specific offsets are signaled by the encoder—one for each EO category, and the signs
of the signaled offsets are implicitly derived from the corresponding EO categories
[
12
,
23
,
24
]. Both EO and BO use four offsets, which limits the number of offsets
to reduce the requirements for a line buffer (the line buffer is explained further in
Sect.
7.4.3
).
7.3.3
Band Offset
Another offset used by the HEVC SAO tool is band offset (BO). In band offset,
one offset is added to all samples whose values belong to the same band (range of