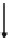Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.10
I_PCM, lossless
and transform skip modes in
decoder
Bitstream
Entropy
decode
I_PCM mode
De-quant
Lossless mode
Transform
skip mode
Inverse
transform
Intra/Inter
prediction
Reconstructed
block
The QP derivation process described in this subsection is used for calculating the
luma QP value. The chroma QP values (one for the Cr component and one for the
Cb component) are derived from the luma QP by using picture level and slice level
offsets and a table lookup.
6.4
HEVC Special Coding Modes
HEVC has three special modes that modify the transform and quantization process:
(a) I_PCM mode [
8
], (b) lossless mode [
31
], and (c) transform skip mode [
19
].
These modes skip either the transform or both the transform and quantization.
Figure
6.10
shows these modes on top of the generic video decoder data flow of
Fig.
6.1
.
In the I_PCM mode, both transform and transform-domain quantization are
skipped. In addition, entropy coding and prediction are skipped too and the video
samples are directly coded with the specified PCM bit depth. The I_PCM mode
is designed for use when there is data expansion during coding e.g. when random
noise is input to the video codec. By directly coding the video samples, the data
expansion can be avoided for such extreme video sequences. The IPCM mode is
signaled at the coding unit level using the syntax element
pcm_flag
.
In the lossless mode, both transform and quantization are skipped. (The in-loop
filter which is not shown in Fig.
6.1
is skipped too.) Mathematically lossless
reconstruction is possible since the residual from inter- or intra-picture prediction
is directly coded. The lossless mode is signaled at a coding unit level (using
the syntax element
cu_transquant_bypass_flag
) in order to enable