Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
newly-added electrode, the
complement
of the graph G
EAA
, referred to as H
EAA
,is
used to reduce the search scope. All the pins corresponds to isolated nodes in H
EAA
are “unavailable pins” and they cannot be assigned to E
neighbor
.
Assume that the number of electrodes on the array is
N
and the number of pins
assigned to the electrodes is
P
. The computing complexity for checking whether
2
). Each time when we assign a pin to E
neighbor
,we
have to verify whether G
EAA
is a simple graph. Thus the computational complexity
of assigning a pin to E
neighbor
is O(
G
EAA
is a simple graph is O(
P
3
) for the worst case. Since all electrodes are
added step-by-step to the set ElectrodesAlreadyAssigned, the overall computational
complexity of the heuristic procedure is O(
P
3
).
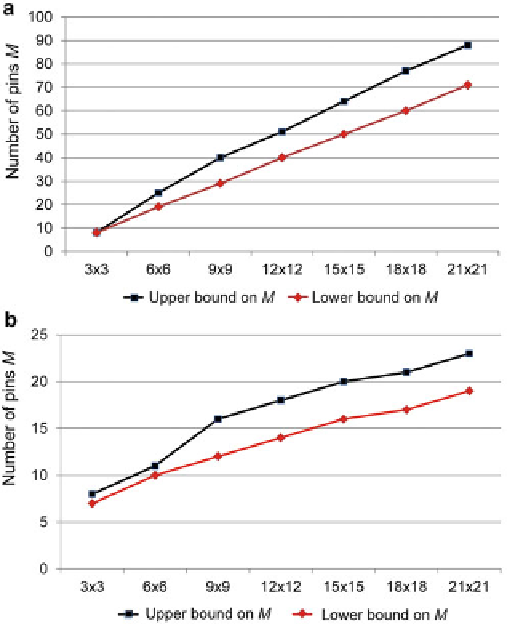
The heuristic algorithm can therefore quickly generate a feasible pin-assignment
configuration, and for each given array layout, the number of control pins derived
by the heuristic algorithm can be used as the upper bound on the number of control
pins. For n
n rectangular layouts and n
n outlined rectangular layouts, Fig.
6.8
a
and b show the lower bounds for the number of pins derived from the theoretical
analysis and the upper bounds for the number of pins derived from the heuristic
algorithm.
P
N
Fig. 6.8
The relationships between lower/upper bounds on pin-counts and the sizes of the
electrode arrays for (
a
) rectangular layouts; (
b
) outlined rectangular layouts