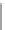Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 4. 3
Bioassay
completion
times
derived
by
PRSA-based
algorithm [
6
]
Completion time (s) derived by PRSA-
based algorithm [
6
] T
i
listed
Bioassay
0
i
2
i
4
i
PCR
26
28
31
35
Interpolation dilution
177
184
195
201
Exponential dilution
195
196
202
208
increases with T
i
. It is important to note that, the synthesis result derived by
the PRSA-based algorithm is deterministic, i.e., the synthesis results determine the
start and stop times of fluidic operations before running bioassays on the fabricated
biochip.
In contrast, the synthesis result derived by the proposed method is semi-
deterministic, the exact start and stop times of fluidic operations will be determined
by feedback from the sensing system when running the bioassays on the fabricated
biochip. If we assume the completion-times of fluidic operations are exactly the
same with the module library defined in [
6
], then the completion times for PCR
bioassays, interpolation dilution bioassays, and exponential dilution bioassays will
be 25, 158, and 182 s, respectively.
4.5.2.2
Response Time in the Presence of Timing Uncertainties
In the re-synthesis algorithm proposed in [
11
], when a sensor detects that the status
of a droplet is inconsistent with the expected result, e.g., an operation is finished
within the pre-determined time, a resynthesis procedure will be performed. The
control software dynamically updates the synthesis steps using a greedy algorithm,
and the operation with unexpected completion time will be re-executed in the
resynthesis result. To compare with [
11
], we first randomly select a fluidic operation,
and assume its execution time is longer than the time defined in the module
library. Then after the resynthesis procedure is triggered, the response time for
the resynthesis procedure in [
11
] is recorded. Here the response time is defined
as the CPU time spent in deriving resynthesis solutions when the timing overshoot
is detected. During on-line resynthesis, all fluidic operations for the bioassay are
suspended.
The simulation is repeated 20 times (using different operations with uncertainty
injected each time). The results show that the proposed algorithm has almost zero
response time while the greedy approach in [
11
] requires around 1 s.