Java Reference
In-Depth Information
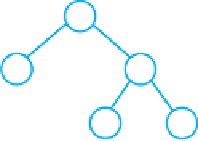
FIGURE 27-4
Before and after a right rotation restores balance to an AVL tree
(b)
(a)
C
N
5
7
N
T
1
3
7
C
T
3
5
9
6
9
T
2
T
3
4
T
1
3
6
T
2
4
Unbalanced
Balanced
The following algorithm performs the right rotation illustrated in Figures 27-3 and 27-4:
Algorithm
rotateRight(nodeN)
//
Corrects an imbalance at a given node
nodeN
due to an addition
//
in the left subtree of
nodeN
's left child.
nodeC =
left child of
nodeN
Set
nodeN
's left child to
nodeC
's right child
Set
nodeC
's right child to
nodeN
return
nodeC
Question 1
Using the notation of Figure 27-3, label nodes
N
and
C
, and subtrees
T
1
,
T
2
,
and
T
3
,
in Parts
c
and
d
of Figure 27-1.
27.3
Left rotations.
Figure 27-5 shows a left rotation in a mirror image of Figure 27-3. The following
algorithm performs this left rotation:
Algorithm
rotateLeft(nodeN)
//
Corrects an imbalance at a given node
nodeN
due to an addition
//
in the right subtree of
nodeN
's right child.
nodeC =
right child of
nodeN
Set
nodeN
's right child to
nodeC
's left child
Set
nodeC
's left child to
nodeN
return
nodeC
FIGURE 27-5
Before and after an addition to an AVL subtree that requires a
left rotation to maintain its balance
(a) Before addition
(b) After addition
(c) After left rotation
C
N
N
C
C
N
h
h
h
+ 1
T
1
T
1
T
2
T
1
T
2
T
3
T
2
T
3
T
3