Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
backward motion vector is derived from the forward motion vector. For an F frame,
besides the conventional single hypothesis prediction mode inaPframe,multi-
hypothesis techniques are added for more efficient prediction, including advanced
skip/direct mode (Shao and Yu
2013
), temporal multi-hypothesis prediction mode
(Ling et al.
2013
), and spatial directional multi-hypothesis (DMH) prediction mode
(Kim et al.
2013
).
In an F frame, an advanced skip/direct mode is defined using a competitive motion
derivation mechanism. Two derivation methods are used, one is temporal and the
other is spatial. Temporal multi-hypothesis mode combines two predictors along the
pre-defined temporal direction, while spatial multi-hypothesis mode combines two
predictors along the pre-defined spatial direction. For temporal derivation, the pre-
diction block is obtained by an average of the prediction blocks indicated by the
motion vector prediction (MVP) and the scaled motion vector (MV) in a second
reference. The second reference is specified by the reference index transmitted in
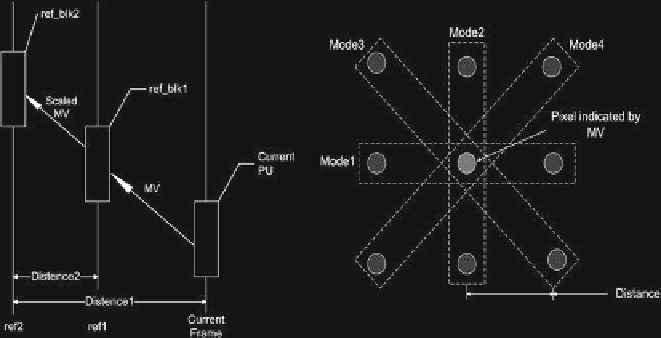
the bitstream. For temporal multi-hypothesis prediction, as shown in Fig.
3.4
, one
predictor
ref
_
blk
1 is generated with the best motion vector
MV
and reference frame
ref
1 searched by motion estimation, and then this motion vector is linearly scaled
to a second reference to generate another predictor
ref
_
blk
2. The second reference
ref
2 is specified by the reference index transmitted in the bitstream. In DMH mode,
as specified in Fig.
3.4
, the seed predictors are located on the line crossing the ini-
tial predictor obtained from motion estimation. The number of seed predictors is
restricted to 8. If one seed predictor is selected for combine prediction, for example
“Mode 1”, then the index of the seed predictor “1” will be signaled in the bitstream.
For spatial derivation, the prediction block may be obtained from one or two
prediction blocks specified by the motion copied from its spatial neighboring blocks.
The neighboring blocks are illustrated in Fig.
3.5
. They are searched in a pre-defined
order F, G, C, A, B, D, and the selected neighboring block is signaled in the bitstream.
Fig. 3.4
Left
temporal multi-hypothesis mode;
Right
spatial multi-hypothesis mode