Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
12.2.3 Primitive-Based Sparse Coding
Sparse representation is an emerging and powerful method to describe signals based
on the sparsity and redundancy of their representations. In sparse representation, each
signal
x
R
d
can be approximated by a linear combination of an overcomplete
dictionary (Elad
2010
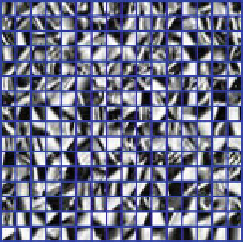
). Figure
12.5
illustrates an example of the dictionary trained by
the 8
(
x
∈
)
8 patches partitioned from
Lena
image. The primitives of dictionaries have the
properties of spatially localized, oriented, and bandpass, which closely correspond
to the characteristics of receptive fields of simple cells (Olshausen and Field
1996
).
As sparse representation is a powerful tool for visual signal representation, efforts
have been devoted to apply it in image and video compression. Existing approaches
such as JPEG and AVC/H.264 can also been formulated in the sparse coding frame-
work, where the transform matrices are fixed dictionaries at both the encoder and
decoder. However, this may lose efficiency when compressing arbitrary images. In
sparse dictionary-based compression, the dictionaries are adaptively learned and
transmitted to the decoder side. Therefore, besides the coefficient coding, compactly
compressing the dictionaries remains an important issue in sparse coding. In Horev
et al. (
2012
), the authors proposed an adaptive image compression framework based
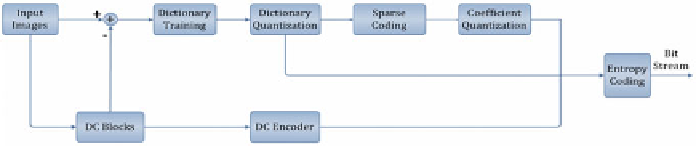
on sparse dictionaries, as illustrated in Fig.
12.6
. The image is first partitioned into
nonoverlapping patches and the DC mean value is subtracted from each patch for
further processing. The DC value for each patch is compressed with the DC encoder.
For each DC-free patch, the K-SVD algorithm is applied to adaptively generate
the dictionary, and OMP algorithm is employed to perform sparse coding for each
×
Fig. 12.5
Trained dictionary with overlapped image patches from
Lena
image
Fig. 12.6
Framework of image compression based on sparse dictionaries (Horev et al.
2012
)