Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
thresholds are derived from the spatial or transform domain of the original frame.
The residuals that are lower than the JND thresholds can be ignored, as the perceptual
quality would not be influenced. By contrast, when the residuals are larger than the
JND threshold, the JND threshold is subtracted from the prediction residual, which
can efficiently reduce the energy of transform coefficients.
In this way, the coding efficiency can be improved from the perceptual quality
point of view. Moreover, the JND-based residual filtering has another advantage
of reducing the computational complexity of the encoder, as fewer coefficients are
coded compared to the conventional coding scheme.
12.2.2.2 Perceptual Quantization
The main source of distortion in video coding is the quantization process, which
directly determines the reconstructed video quality with the quantization parameter.
Therefore, how to select the optimal quantization parameter for each coding frame,
unit, and frequency has been a hot research topic in perceptual video coding.
As the visual sensitivity can be reflected by the JND threshold, the local quanti-
zation parameter adjustment scheme with JND is proposed. For example, in Chen
and Guillemot (
2010
), researchers applied the FJND model in the quantization para-
meter adjustment process. For the MB with lower JND value, smaller quantization
parameter should be used, as it is more sensitive to the HVS.
Though JND can efficiently characterize the near-threshold distortions, in video
coding, the distortion is usually visible. Therefore, it is more accurate to formu-
late the visual sensitivity from the suprathreshold computational models. In Tang
et al. (
2006
), the spatial-temporal sensitivity models are applied in rate control. In
Chen et al. (
2012
), adaptive quantizationmatrix selection and updatingmethod is pro-
posed, in which the macroblock is classified into three types: no frequency weighting,
detailed preserving, and undetailed. In Wang et al. (
2013
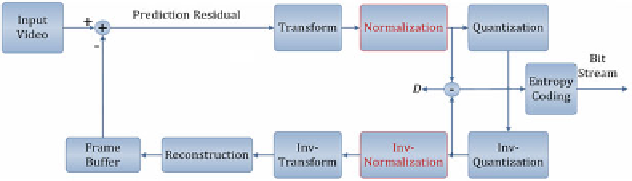
), the divisive normalization
idea is applied in video coding, where the frame residuals are transformed into a
perceptually uniform space by adjusting the quantization parameters for each MB.
The proposed framework is shown in Fig.
12.3
, and it has also been implemented
into AVS2 coding standard. Experimental results show that 5-7% bitrate reduction
can be achieved in terms of SSIM.
The nonuniform distribution of the cone receptors and ganglion cells in the retina
makes the attention point sampledwith the highest resolution, and it rapidly decreases
Fig. 12.3
Framework of the divisive normalization-based perceptual video coding framework