Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
11.1.2 Full Reference Image Quality Assessment
For FR-IQA, the pristine reference image is fully available. In the literature, themajor
efforts are focused on the FR-IQA models. The most popular FR-IQA method is the
Mean Square Error (MSE) or Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), which directly
computes the pixel-wise distance between the reference and distorted images. It is
appealing in many applications due to its simplicity and clear physical meaning.
However, it has been long criticized for the poor correlation with the perceptual
experience of HVS (Girod
1991
). Therefore, more accurate metrics that consider the
HVS characteristics have been studied, including Structure SIMilarity (SSIM) (Wang
et al.
2004a
), Visual Information Fidelity (VIF) (Sheikh and Bovik
2006
), Visual
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (VSNR) (Chandler and Hemami
2007
), Feature SIMilarity
(FSIM) (Zhang et al.
2011
), and Gradient Magnitude Similarity Deviation (GMSD)
(Xue et al.
2014
) etc. In this section, we will briefly introduce these quality metrics
and discuss their design principles.
11.1.2.1 SSIM
SSIM and its variants Multiscale SSIM (MS-SSIM) (Wang et al.
2003
), Information-
Weighted SSIM (IW-SSIM) (Wang and Bovik
2011
) can provide a good approxi-
mation of the subjective scores, and have been successfully used in a wide range of
applications. The basic idea is that the HVS is highly adapted to perceive structural
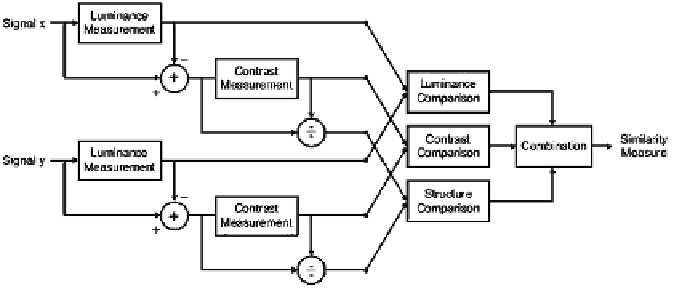
information from the natural scene. Based on this assumption, a novel framework of
IQA is proposed as shown in Fig.
11.1
. Suppose
X
and
Y
are the original and degraded
images, respectively, the similarity of their structural information can serve as a quan-
titative metric in predicting the perceptive quality of the distorted image. This IQA
scheme has three components: luminance, contrast, and structure comparisons. First,
the luminance similarity is computed by the mean intensity as follows,
Fig. 11.1
Illustration of the SSIM index