Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
data among hundreds and thousands of consecutive pictures. In this case, the back-
ground can be modeled and then utilized by the video codec to remove the “scenic
redundancy” in these pictures, consequently leading to the remarkable decrease of
the total bit rate (see Fig.
10.3
a). In IEEE 1857 surveillance groups, the background
model is represented as a specially encoded I-picture (hereafter called G-picture)
and can be encoded as a nondisplay frame into the steam to guarantee the decoding
match. As shown in Fig.
10.3
b, the total bit rates should be the same as the traditional
coding method in the initial stage, and decrease quickly in the following process.
Overall, they can double the surveillance video coding efficiency compared with
AVC/H.264 HP.
In particular, IEEE 1857 surveillance groups feature the following technological
characteristics to support the intelligent video coding:
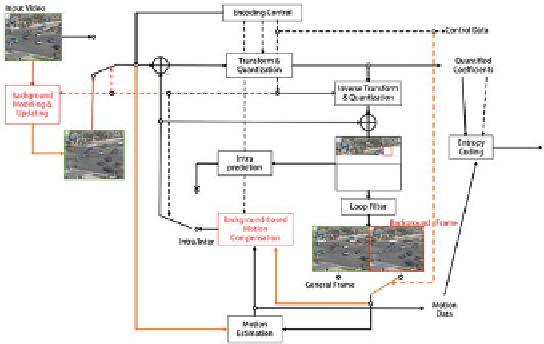
1. A novel model-based coding framework: IEEE 1857 surveillance groups add the
background-based prediction and coding technology into the traditional hybrid
video coding framework. As shown in Fig.
10.4
,this novel coding framework
Fig. 10.3
a
Surveillance video coding with background modeling,
b
the ideal bit rate curve
Fig. 10.4
The background model-based coding framework used by IEEE 1857 surveillance groups