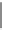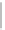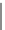Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
B
n
V
obsv
i
B
g
=
argmin
b
J
(
b
,
)
|
b
∈
(8.5)
i
=
0
where
b
is arbitrary modeling background frame in the available set of background
frames
B
, and
J
V
obsv
i
is a function for calculating the rate-distortion cost of
encoding the
i
th observed scene
V
obs
i
with b as reference. Because
B
g
is only
updated after an
LGOP
, the first feature is concluded as
periodically background
updating
.
To evaluate the efficiency of different common BgModeling methods for sur-
veillance video coding, four typical methods are implemented and embedded into
AVC/H.264 baseline profile encoder (BP). The four methods are the Mean Shift
(namely MS) proposed in Liu et al. (
2007a
), the popularly used Gaussian running
average (RA), and the Gaussian Mixed Models (Haque et al.
2008b
)using1or5
models for each pixel (GMM-1 or GMM-5). Corresponding Encoders are namely
BP-MS, BP-RA, BP-GMM-1, and BP-GMM-5. The encoding results on different
CIF&SD surveillance sequences, provided by AVS workgroup, can be seen from
Table
8.3
. As is shown, comparing with the BP encoder without BgModeling, BP-
GMM-5 obtains the highest performance.
For BgModeling in surveillance video coding, as is referred, performance, mem-
ory cost, and running time are the same important factors. The calculation for their
memory cost in each pixel position is listed as follows.
•
(
b
,
)
RA: one current pixel with type of char and one float-precision mean value for
each pixel should be buffered.
•
GMM-X: besides the buffered input pixel, aGMMmodel is required to be buffered.
The model is composed of double-precision mean value, variance, and weight.
Moreover, an 8-bit value should be stored to count the number of matched points
for each GMM model.
•
MS: Mean shift-based algorithms usually buffer all the training frames and very
fewadditional temporal variables are used for the clustering and sorting operations.
Supposing the number of training frames is denoted by M
120, from the above
analysis of RA, GMM-X and MS, the memory cost for each algorithm is listed in
Table
8.4
.
=
Table 8.3
BgModeling based BP versus BP on PSNR gain (dB)
BP-x on SD
Crossroad
Overbridge
Bank
Office
Average
GMM-1
0.92
1.37
1.13
0.40
0.96
RA
1.22
1.73
1.71
0.58
1.31
MS
1.26
1.81
1.68
0.74
1.37
GMM-5
1.34
1.94
1.79
0.88
1.49
BP-x on CIF
Crossroad
Overbridge
Snowgate
Snowroad
Average
GMM-1
0.79
0.50
1.13
0.91
0.84
RA
0.93
0.80
1.75
1.34
1.21
MS
1.01
0.89
1.62
1.23
1.19
GMM-5
1.22
0.95
1.76
1.51
1.36