Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 8.4
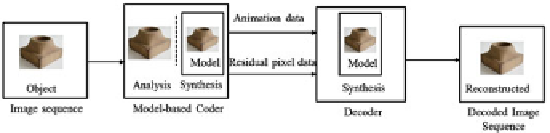
Principle of model-based coding (MBC)
Fig. 8.5
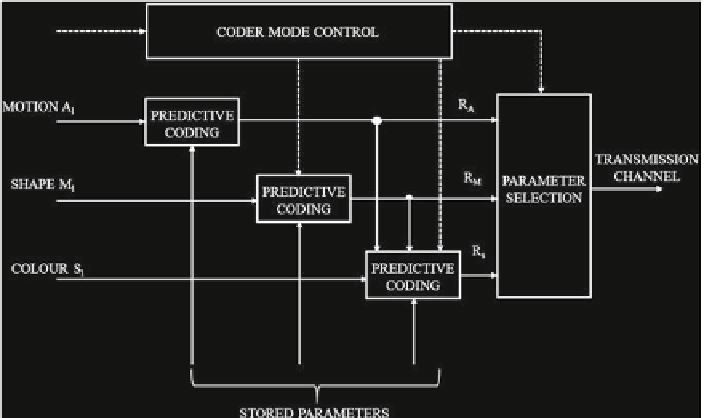
Block diagram of the parameter coder
location, and motion, etc. As shown in Fig.
8.4
, a model-based coder is composed of
two parts, including analysis and synthesis. First, the information of the segmented
objects are analyzed and transmitted to the decoder side called animation. These
abstracted model parameters may be coded with predictive coding or hybrid coding
methods (Musmann
1993
),asshowninFig.
8.5
. Moreover, inMusmann's viewpoint,
MBC is extended to be a more generalized coding system which covers almost all
kinds of coding methods, including pixel model-based coding, block motion model-
based coding, and object model-based coding, etc. In this topic, we would follow
Musmann's viewpoint to divide model-based coding into nine different levels, as
shown in Table
8.1
.
From Table
8.1
, we can see the evolution of model-based coding, from the statisti-
cal pixel and block, to the geometric partition and structural segmentation, and from
the content aware object to the understanding of the content including knowledge and
semantic, and from the perceptual sensing to the intelligent vision. In the historical
evolution of MBC, pixel model-based video coding, e.g., PCM, was ever used for
early memory and computation resources limited applications, and it was replaced