Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
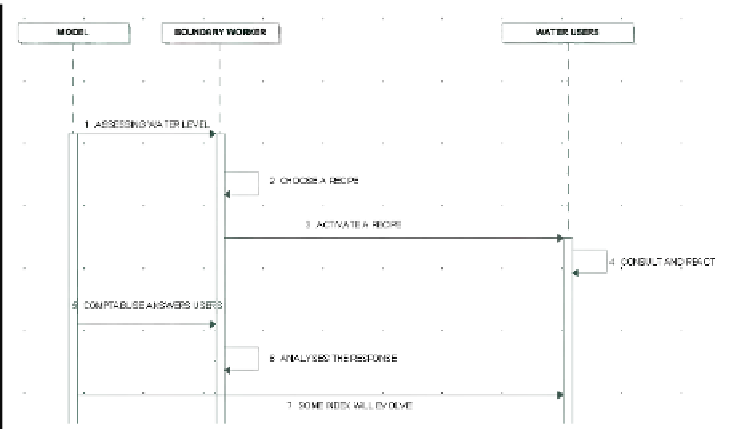
Fig. 6.
Sequence diagram
He will activate a recipe and send the message to water users. He consults this
message and responds to the recipe sent indicating whether or not his participation to
the recipe. The boundary worker will take into account the user responses and some
index will increase or decrease depending on what the recipe implied.
The user answer to a recipe sent by the boundary worker is subjected to various
tests. To begin, the user will observe if he has received in his “mailbox” a recipe
request. For example the recipe is that the water level in the river is deficient. So the
users are encouraged to reduce their water withdrawals. The users will make a first
test and observe if their own assessment of water level requires a reduction of their
practices. If they agree they reduce their activity, but otherwise they will make a new
test. Each user will test his confidence index on the boundary worker. If this index
exceeding a determined threshold the users will accept the recipe otherwise he will
not change anything.
5
Conclusion and Perspective
This paper discusses the creation of an ABM which is based on empirical data.
Qualitative data are involved in the construction phase of the model and will describe
research questions, rules of behavior, interactions between agents and some scenarios
to simulate. This empirical work has resulted in the development of a recipe list which
has been validated by a boundary worker.
This framework will also help to prepare a return to the field and to conduct a
revision of the ABM. In our case study it seems clear that following the first
simulations new questions appear and force us to return to the field to ask for some
boundary workers. The return phase seems necessary to calibrate the model as finely