Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
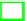
Tabl e 1.
Mixed strategy equilibrium in simplified DIY-L
NM
1
2
3
4
3 3 0.464102 0.267949 0.267949
3 4 0.457784 0.251643 0.145286
0.145286
4 3 0.448523 0.426330 0.125147
4 4 0.447737 0.424873 0.125655 0.00173500
Then, each game form has a unique mixed strategy equilibrium. Table 1 gives
the mixed strategy equilibria in cases of (
N,M
)=(3
,
3)
,
(3
,
4)
,
(4
,
3)
,
and
(4
,
4).
3
3 Computational Experiments
3.1 Setup
There are two kinds of players, adaptive learning (AL) agent(s) and quasi ficti-
tious play (QFP) agent(s), in DIY-L
4
. AL agents use only their attractions for
their decision-makings, namely choose one pure strategy. On the other hand,
QFP agents store the past possible, but not observable, plays of their opponents
and then form their adaptive beliefs to make a decision:
-
AL agents
AL player
i
(
i
=1
,
···
,N
) has a propensity
w
i,k
(
t
)for
k
-th strategy (integer
k
)
s
i
(
k
=1
,
,M
) at time
t
. Before the game, she is assumed to have
non-negative propensities for all the strategies, namely
w
i,j
(0) =
w
i,k
(0)
···
≥
0for
j
=
k
.
At every turn, she chooses one pure strategy in accordance with the following
exponential selection rule
exp(
λ
a
·
w
i,k
(
t
))
p
i,k
(
t
)=
M
k
=1
exp(
λ
a
·
w
i,k
(
t
))
where
p
i,k
(
t
) is the selection probability for strategy
s
i
and
λ
a
is a positive
constant called sensitivity parameter [4,7].
3
A perfectly rational player follows this table. For instance, in (
N,M
)=(3
,
3) DIY-
L, she submits 1
w.p.
0.464102 and 2 and 3
w.p.
0.267949. Ostling et al. have a
succinct algorithm to calculate mixed strategy equilibrium in this setup [12]. The
mixed strategy equilibrium in DIY-L with
N ≥
3and
M
= 2, namely binary choice
game, is independent of the number of players; The mixed strategy equilibrium is
0.5 for each integer. Hence, we have omitted this kind of game setup.
4
One of the anonymous referees questioned why we employed the learning models in
economic literature, not in computer sciences such as LCS or XCS. It is true that
LCS and XCS are quite powerful learning models for exploration, but such models
do not explain real behaviors and learnings of individuals reported by Ostling et al.
[12]. Thus, in accordance with the discussions by Brenner [2], adaptive learning and
quasi fictitious play are used.