Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
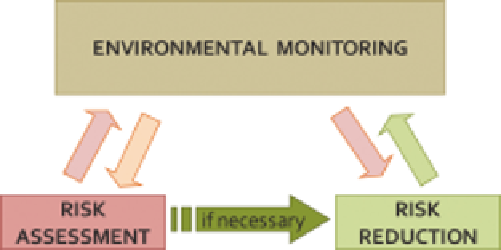
Figure 11.2
Dynamic relationship between environmental monitoring, risk assessment and risk
reduction.
-
Diminishing uncertainties of data and information;
-
Collecting time-series data on the environment and evaluating the trends, the
directions and rate of changes;
-
Using early warning methods, as close to the source and as early in time as
possible;
-
Using integrated assessment methodology, establishing and applying the most ade-
quate combination of mathematical, physical, chemical, biological and ecological
methods (optimal tool box);
-
Using a stepwise assessment methodology with optimal tiering (pursuing maximal
information, maximal technological, time- and cost-efficiency);
-
Using innovative risk reduction measures, efficient environmental remediation
including natural attenuation-based,
in situ
and ecological methods;
-
Using integrated and complex remediation by applying physical,
chemical,
biological and ecological remedial tools;
-
The
combination
of
prevention,
restriction
and
remediation
for
risk
reduction;
-
Collecting information on the entire range of site assessment, monitoring
and remediation technologies with regard to their applicability, adequacy and
suitability;
-
Applying a comparative evaluation before selecting the most proper risk assess-
ment and reducing approach;
-
Developing a uniform verification system for the characterization of environmental
technologies;
-
Handling environmental monitoring, risk assessment and risk reduction in an
integrated and dynamic way as shown in Figure 11.2;
-
Using demonstrated and verified methods and technologies;
-
Developing decision-support tools for every step of decision making;
-
Communicating environmental risk and the management steps in an efficient and
ethical way;
-
Considering social, economic, cultural and ethical issues besides the scientific and
technological information as illustrated in Figure 11.3.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search