Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
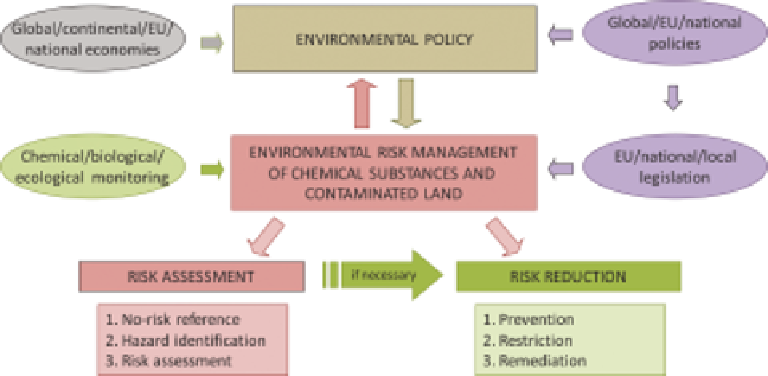
Figure 8.9
Tasks and activities of environmental risk management.
Figure 8.9 summarizes the context of the compartment of environmental manage-
ment. It shows that ERM is the key tool of environmental policy and environmental
management. ERM has two main facets: risk assessment and risk reduction. If risk is
higher than acceptable, risk reduction is necessary. ERM is supported by legislation
and environmental monitoring. Legislation establishes the uniform framework for effi-
cient risk management, while monitoring provides management with current data and
long-term trends on the environment.
9.1 Environmental legislation in the context of
chemical pollution
Legislation encourages and guides parties to successfully negotiate the narrow path
between the needs and requirements of the environment, human health, economic
growth and political stresses. The contradiction between the need for flexibility and
a case-by-case approach to tackle environmental problems, and the relative rigidity
of legislation, can be solved by a high-level understanding of the environment and
the intention to keep the environment in the best possible condition. Ideal legislation
involves a continuously expanding framework of knowledge and a wide selection of the
best available techniques and technologies. Environmental legislation and ERM should
be interactive, dynamic tools based on up-to-date science and innovative management.
See also Chapter 2 of this Volume.
9.2 Environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring, on which ERM mainly rests, is a technical tool with con-
tinuously developing strategies. A historical report on the state of the environment is
the most important input for efficient management. The data time series ensure better
evaluation and statistics, and allow a dynamic interpretation of environmental data.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search