Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
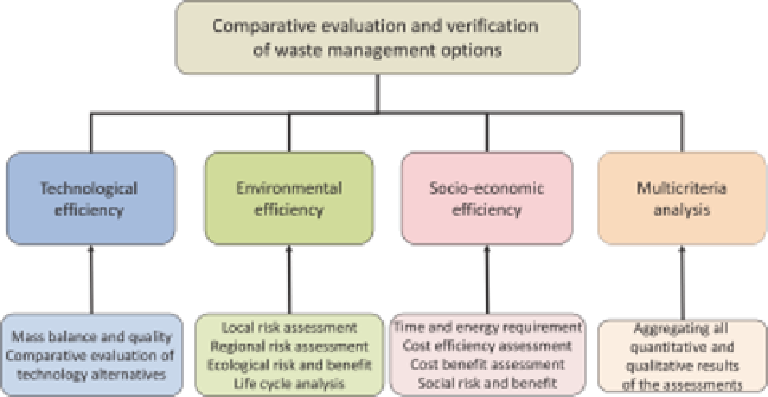
Figure 6.9
Evaluation of the waste management options and waste treatment technologies.
technology, it should be verified based on monitoring data. Monitoring should cover
the following:
-
Technological parameters (temperature, pressure, material fluxes, mass of addi-
tives, produced product quantity and quality, etc.);
-
Environmental parameters (emissions into air and water,
residues and their
treatment, ecological impact parameters);
-
Socio-economic parameters (used energy, cost of additives, price of the product,
number of employees, satisfaction of local population, etc.).
The comparative evaluation of the management options to support the selection of
the best possible technologies can quantitatively show the alternatives' risks and bene-
fits and provide optimum waste management. The subsequent evaluation of the applied
technology verifies the technology and its performance based on monitoring data.
REFERENCES
40 CFR Part 260 (2012)
Hazardous waste management system: general
. [Online] Available
from: http://federal.eregulations.us/cfr/title/1/14/2013/title40/chapterI/part260 and www.
wbdg.org/ccb/EPA/40cfr260.pdf. [Accessed 17th August 2013].
40 CFR Part 261 (2012)
Identification and listing of hazardous waste.
[Online] Available
from:
http://federal.eregulations.us/cfr/title/1/14/2013/title40/chapterI/part261.
[Accessed
7th August 2013].
Adams, E., García-Sanchez, A., Santos, F., Velázquez, E. & Adams-Melendez, M. (2007) Immo-
bilization of mercury in soils of Venezuela using phospho-gypsum and sulphate-reducing
bacteria, First International Meeting on Microbial Phosphate Solubilization
. Developments
in Plant and Soil Sciences
. 102, 333-336.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search