Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
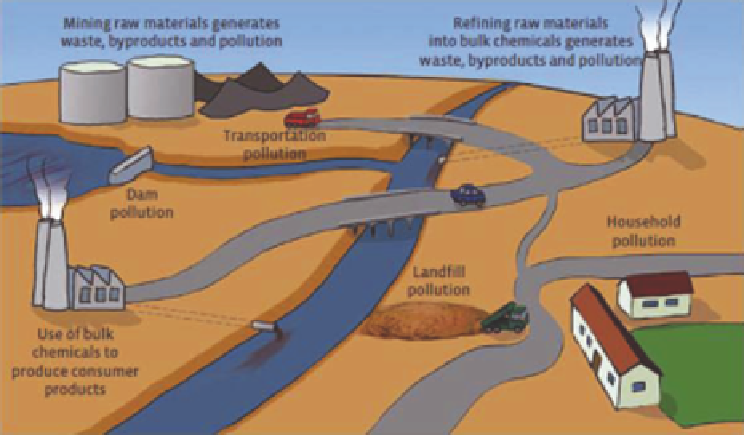
Figure 5.1
Environmental impacts of mining.
solid waste and slurry contaminates the mining area and its surroundings significantly.
It also harms the whole catchment the mine belongs to. Uncontrolled disposal of
large amounts of waste in solid or slurry form may pose a long-term hazard to the
environment, turning green valleys into waste repositories. Water level oscillations
in surface waters deteriorate the equilibrium of both subsurface and surface waters
impacting the whole water system. The static stability of mine waste (tailings) dams
and the sealing potential of waste repositories are key factors in protecting the environ-
ment against chronic emissions or sudden accidents. Tailings are fine-grained residues
of the milling process in which the desired raw materials (e.g., metals) are extracted
from the mined rock and appear, due to mixing with water during this process, as
slurries. Figure 5.1 shows the general environmental impacts of mining.
In terms of environmental impacts, mining results in emissions into air, water and
land and it leaves behind large amounts of waste. Mining produces solid wastes and
disrupts the soil surface. The solid waste includes overburden material (soil, waste
rock and vegetation) from surface mining, material from shafts and non-ore materials
included in deposits from underground mining or tailings from beneficiation processes.
The extraction process has detrimental impacts on air quality resulting in airborne
particulate matter (PM) from the use of explosives and earth moving. Fine PM of the
exhaust from heavy equipment also causes air pollution. Mineral processing results
in dust from sizing operations and combustion products from heat sources in thermal
processes. Volatile organic compounds are emitted into the air by solvent extraction
processes or in the vapors associated with the use of fuel for heavy equipment.
Surface and groundwater quality is affected by acidic discharges from waste rock
piles and tailings ponds (acid rock drainage or ARD) containing naturally occurring
sulfides, from water percolating through abandoned mines, which is called acid mine
Search WWH ::

Custom Search