Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of air saturation. It was demonstrated that hyperoxic conditions
(pO
30%) were preferable for the better proliferation of hESCs,
enhancing their energetic metabolism. Using this culture system,
they achieved hESC expansion culture with a 12-fold improvement
of final cell yield in comparison with conventional static cultures.
Leung et al
2
implemented the ESC/iPSC expansion culture by a
stirred suspension culture system using two hESC lines, HES-2
and HES-3, and one hiPSC line, IMR90 [20]. They used Matrigel-
coated DE53 (Whatman) as a microcarrier. HES-2 cells could be
successfully expanded maintaining pluripotency, with improvement
of their proliferation in comparison with a static culture. On the
other hand, in the case of HES-3 cells and IMR90 cells, shear stress
due to stirring of the culture system reduced their pluripotency and
proliferation by promoting differentiation. The result indicates that
some ESC/iPSC lines are shear sensitive, and thus the shear stress
in a stirred suspension culture system should be reduced as much
as possible to establish this system as a robust and general culture
method for undifferentiated ESC/iPSC expansion.
.
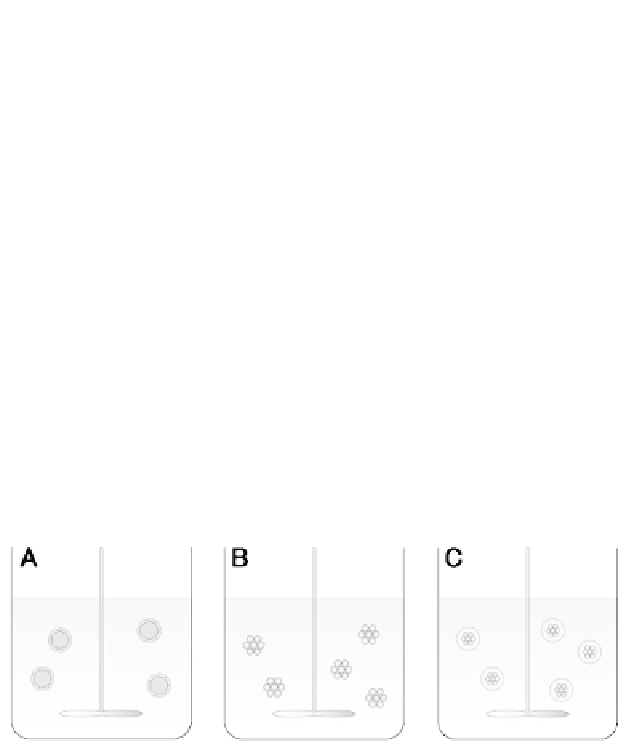
Figure 2c.2
Three aspects of hES/iPSC stirred suspension culture. (A)
Stirred suspension culture of hES/iPSCs with microcarriers.
(B) Stirred suspension culture of hES/iPSC aggregates. (C)
Stirred suspension culture of encapsulated hES/iPSCs.
The interaction between ESCs/iPSCs and the surface of a culture
substrate are considered important factors to maintain the cells'
pluripotency and self-renewal capacity. However, there are also
attempts to expand undifferentiated ESCs/iPSCs as cell aggregates
in a stirred suspension culture system without microcarriers (Fig.
2c.2B). The formation of ESC/iPSC aggregates generally promotes
their differentiation. Krawetz et al. prevented the differentiation of
hESCs in aggregates using rapamycin, a kind of immunosuppressant,