Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
170
160
150
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Accumulated load
Dry and wet
Dry
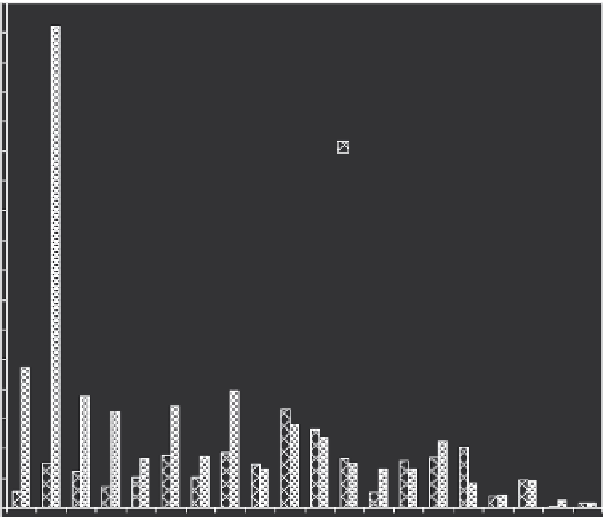
Figure 8.11
Mean composition of OCs in dry and bulk (dry and wet) atmospheric
deposition over the course of 1 year in Teide. The intervals represent the standard deviation.
As observed, the compounds that are the most volatile and also associated with wet
precipitation have the greatest deposition (based on van Drooge
et al
. 2001). Note that
these results are consistent with those shown in Fig. 8.7, which were obtained in other
locations.
In the boreal forest zone of Northern Europe, climate change may lead to
methylmercury concentration increases in fish. Thousands of lakes in Scandinavia
already have mercury levels in fish that exceed the health guideline of 0.5 mg kg
−1
,
making them unsuitable for human consumption. In this region, climate models
predict winter precipitation increases which may lead to higher groundwater
levels and more water to flow through organic-rich soil horizons where a large
fraction of the soil-bound mercury is accumulated, potentially causing direct
mobilization of mercury and methylmercury. Changing redox conditions and
higher release of DOC and nutrients may further enhance the concentrations of
methylmercury in aquatic ecosystems.
Manipulation of precipitation and hydrology at Gårdsjön, an experimental lake
site in south-west Sweden, has shown increases in both total mercury (i.e. sum of
all forms of mercury) and methylmercury in run-off water. The transport of total
mercury was found to be proportional to the increases in run-off amounts whereas





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search