Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
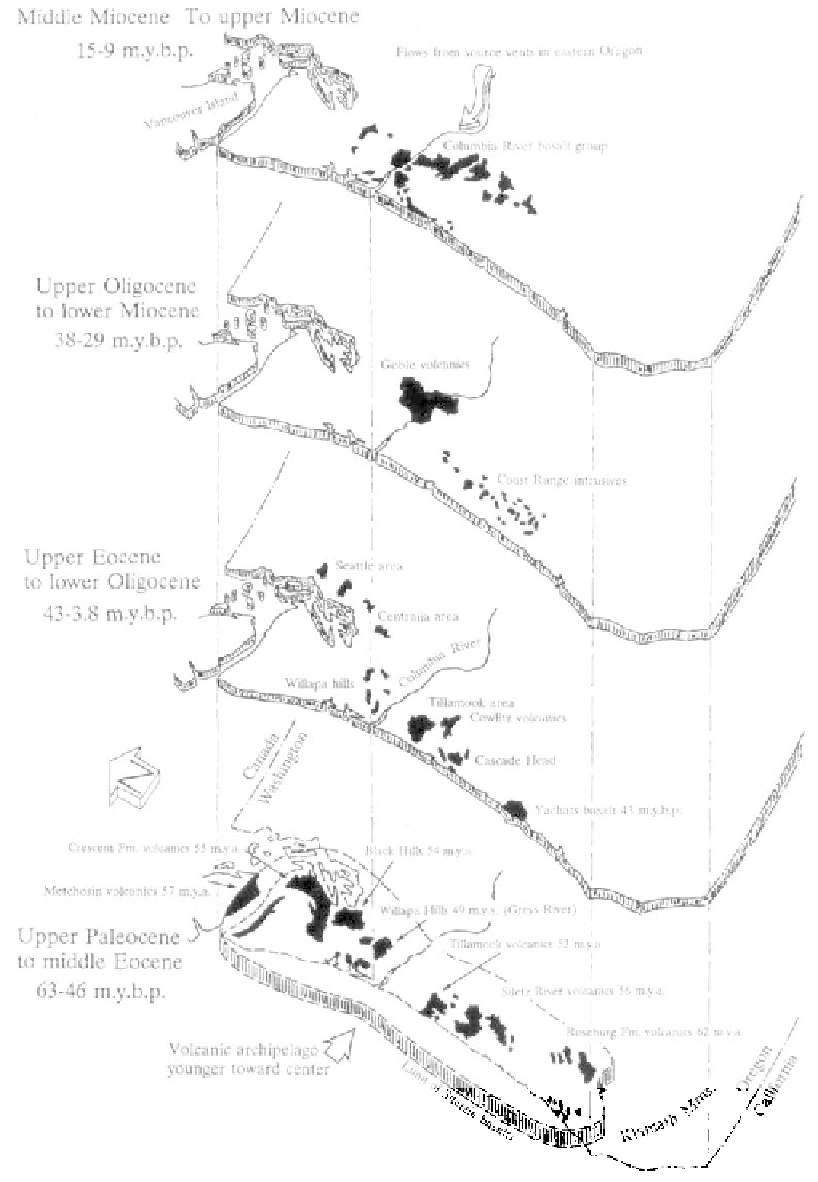
Volcanic rocks of the Oregon and Washington
Coast Range (Armentrout and Suek, 1985)
because of their size and shape, which formed when
clockwise direction with a pivotal point in northwest
lavas were extruded underwater onto an ocean floor.
Washington. By Oligocene time backarc spreading had
With lava thicknesses up to 2 miles, the island
moved the block close to the position of the present
chain was far too large to be simply overridden or
day Cascades. Beginning in the Miocene epoch, 20
subducted, thus it was incorporated into the larger
million years ago, a second rotational phase began.
North American landmass following collision. During
With the process continuing to the present, it is
the 50 to 42 million year interval, the still-forming
estimated that the Coast Range has rotated 51 degrees
Coast Range block began to rotate westward in a
since late Eocene, up to 44 degrees since the middle