Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Pleistocene less than a million years ago. The Clackam-
as River fault projects northwesterly to merge with the
Portland Hills fault zone. One of the most extensive
structures across the Cascades is the Eugene-Denio
fault system. Recognized initially as a lineament, the
fault zone begins southeast of Eugene on the west side
of the Cascades and runs through the range appearing
again at Walker Rim east of the mountains. The
dominant period of movement along this fault dates
back to 22 million years ago.
Running southwesterly into the Cascades from
central Washington, the Yakima structural belt is a
series of late Miocene east-west by southwest-northeast
trending gentle folds in the Columbia River lavas.
Along the banks of the Columbia River, the fold belt
appears in cross-section where the gorge cuts through
the Ortley and Bingen anticlines and Mosier syncline.
These folds fit into a broad southwest-northeast
trending structure called the Columbia trans-arc
lowland which subsided before the Columbia River
basalt flows invaded the gorge more than 16 million
years ago. This broad trough served as a natural
conduit for these lavas as well as for the Columbia
River itself. In the Willamette Valley to the west, a
farther extension of this lowland is the Sherwood
trough.
From the southwest corner of the state, the
Klamath-Blue Mountains lineament projects through
the Cascades to run parallel to and just north of the
Blue Mountains anticline. Whereas many of the
lineaments are now recognized as large-scale faults, the
Klamath-Blue Mountains structure is of unknown
origin.
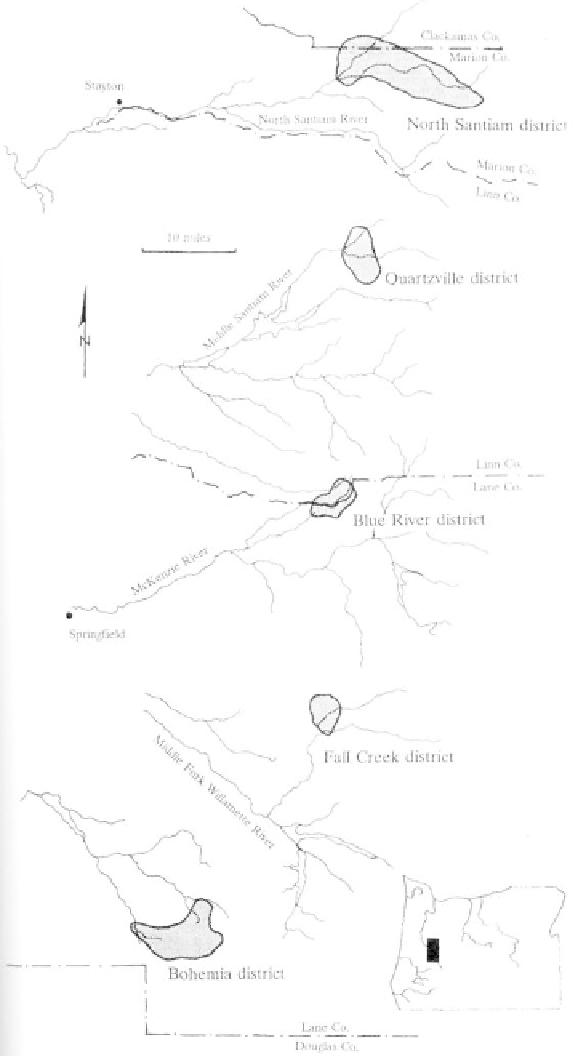
Mining districts situated along the eastern margin of
the Western Cascades (after Ferns and Huber, 1984)
of unclear origin, running diagonally through the range.
From the southeast, the McLoughlin, Eugene-Denio,
and Brothers fault zones extend from the Basin and
Range and High Lava Plains provinces to the Cascades.
The poorly understood McLoughlin belt of faults
terminates in the southern High Cascades somewhere
in Lake or Jackson counties. Toward the southeast, the
Clackamas River belt of faults may be an extension of
the Brothers fault zone which was active well into the
Jawbone Flats, constructed in 1932 as a mining
camp, was part of the North Santiam mining district
(photo Oregon Dept. Geology and Mineral Indus-
tries).