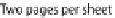Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5.3
Example layouts of
printouts
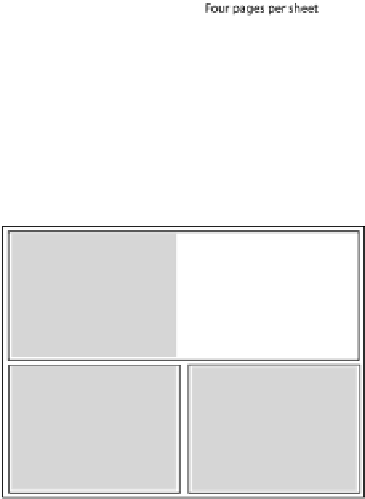
Fig. 5.4
Example of physical
and logical pages
Physical page
Logical page
Page of the digital document
Empty area
Logical page
Logical page
Page of the digital document
Page of the digital document
vides for reserving empty space for taking notes beside, above, below or around the
document page. Annotations are stored in a generic representation, independently
of the currently chosen print layout.
In contrast to other applications, which usually model handwritten annotations as
being located on one single page, our model supports annotations that span multiple
pages. This is particularly important because one physical page can contain multi-
ple logical pages and users frequently write over the boundaries of individual logical
pages. It would not be acceptable to cut these annotations into two or more separate
fragments. Instead, our model keeps these annotations intact and treats them as one
single annotation. The x and y coordinates of the individual samples of the annota-
tions are normalized to be in a
[
0
..
1
]
range, where the coordinate
(
0
,
0
)
denotes the
upper left and
the lower right corner of the bounding box of the annotation.
This makes the modeling independent of the actual position of the annotation on a
page. For each logical page the annotation is located on, it contains some context
(
1
,
1
)