Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1.5.
The automation of the DMKD process using XML based technologies.
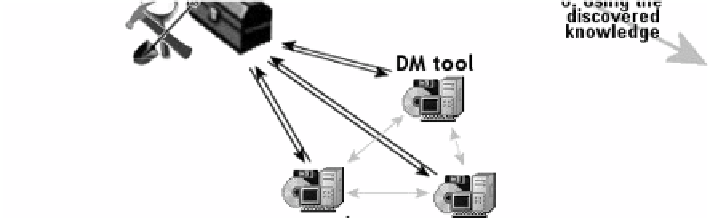
A DM step may use a DM toolbox that integrates multiple DM tools [45]. The
DM toolbox architecture, based on XML, is shown in Fig. 1.6.
The idea of implementing DM toolboxes arises from a simple observation that
no single DM tool performs well on all types of data. XML and XML-based
technology like SOAP and UDDI make the implementation of such toolboxes easy.
First, the DM tools are registered as Web services using the UDDI registry. The
DM toolbox performs a series of steps to generate knowledge from data. It loads
the data from a database, and then using UDDI and WSDL descriptions it scans
for DM tools that are available and suitable for particular analysis. Next, it
communicates with selected DM tools, provides them with the data, and receives
the results of analyses. Finally, it processes the results and stores them in the
knowledge database.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search