Database Reference
In-Depth Information
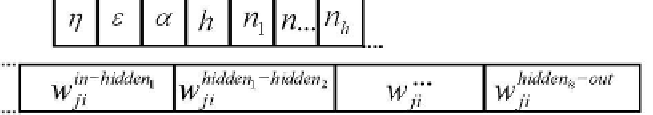
Fig.7.17.
Genotype of neural networks.
7.4.3.2 Finding Network Structures by GA
In this section, we applied the method described in [18] to search for an optimal
network structure by GA. We explain the genotype and genetic operators.
Genotype Representation
Figure 7.17 shows the chromosome with some learning parameters η , ε , α ,
and
n
in Table 7.9 and connection weights
(
)
w
−
1
0
≤
w
≤
1
. Here
n
is
j
i
j
i
the number of hidden neurons.
Genetic Operators
GA search involves three kinds of genetic operators: selection, crossover, and
mutation. Here the selection is implemented as a combination of elite strategy and
roulette selection. The ratio of the chromosomes copied to the next generation by
elite strategy is
P
e
. That is, 10% of the chromosomes are selected using
elitist strategy, and the remaining individuals are selected using roulette wheel
selection. Successively two individuals are selected to make a crossover operation
according to their fitness values. Crossover operation generates new offspring
from the two selected individuals. Each gene representing a network is shown in
Fig. 7.17. In this investigation, we employ the uniform crossover. For the mutation
operation, [18] defined two types of mutation rate: local mutation
=
0
.
P
and global
mutation
m
P
. The local mutation gives a small perturbation as shown in Table
7.10 to search in the neighborhood of local minima. On the other hand, the global
mutation expands the search space by the parameters in Table 7.11.
ml
Table
7.9.
Learning parameters of a neural netwo
rk.
ˤ
0
<
η
≤
1
.
η
∈
R
0
<
ε
≤
1
.
0
ε
∈
R
ˢ
0
<
α
≤
1
.
0
α
∈
R
˞
n
2
≤
n
≤
20
n
∈
N

Search WWH ::

Custom Search